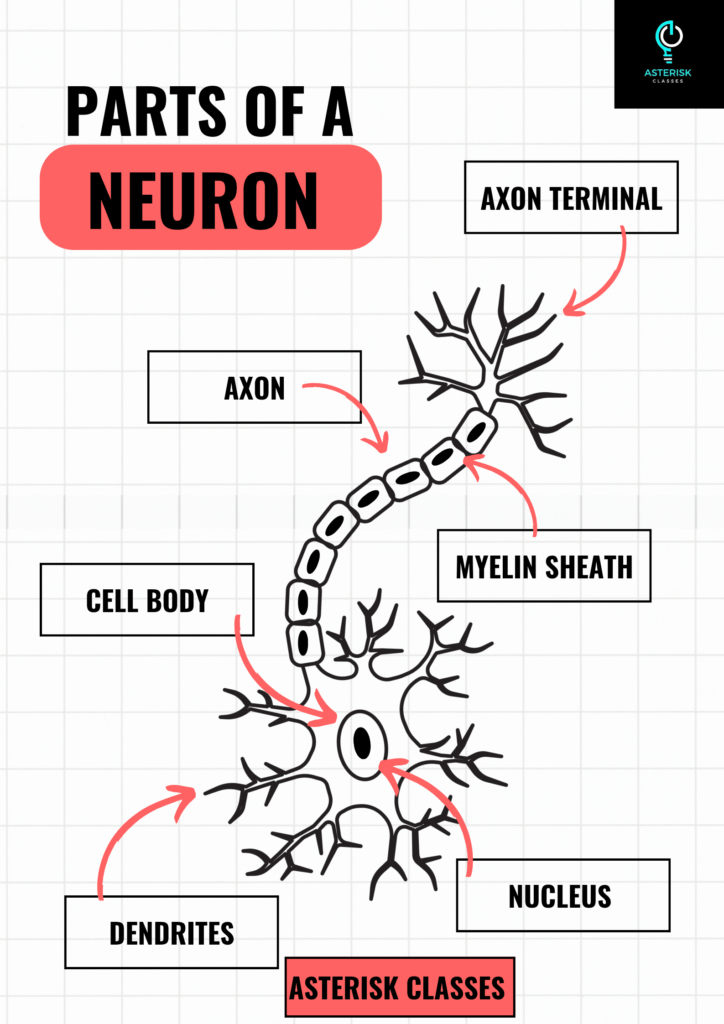
✅Neurons are the core components of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting information throughout the body.
✅Structurally, a neuron consists of three main parts: the cell body, dendrites, and axon. The cell body contains the nucleus and is essential for the neuron’s metabolic activities.
✅ Dendrites are tree-like structures that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them to the cell body.
✅ The axon is a long, slender projection that carries electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
✅Some axons are covered with a myelin sheath, which accelerates the transmission of electrical signals.
✅At the end of the axon are the axon terminals, which form synapses with other neurons or target cells. This synaptic junction is where neurotransmitters are released to propagate the signal to the next neuron.
Some Important Facts about the Neurons
Neurons are the core components of the brain and nervous system, responsible for carrying messages throughout the body.
Here are five fascinating facts about them:
Firstly, the human brain contains approximately 100 billion neurons, each with the ability to form thousands of connections with other neurons, leading to a complex network of as many as 10 trillion connections.
Secondly, neurons come in a variety of shapes and sizes, with the longest human neuron extending from the base of the spine to the toes.
Thirdly, unlike most cells, neurons cannot regenerate, which makes brain injuries particularly challenging to heal.
Fourthly, the speed at which neurons transmit information is astonishing, ranging from 0.5 meters per second to an impressive 120 meters per second.
Lastly, the brain’s energy consumption is immense, with neurons generating between 10 and 25 watts of power, enough to light a low-wattage LED bulb.
These facts not only highlight the complexity of the human body but also the remarkable efficiency and power of our nervous system.