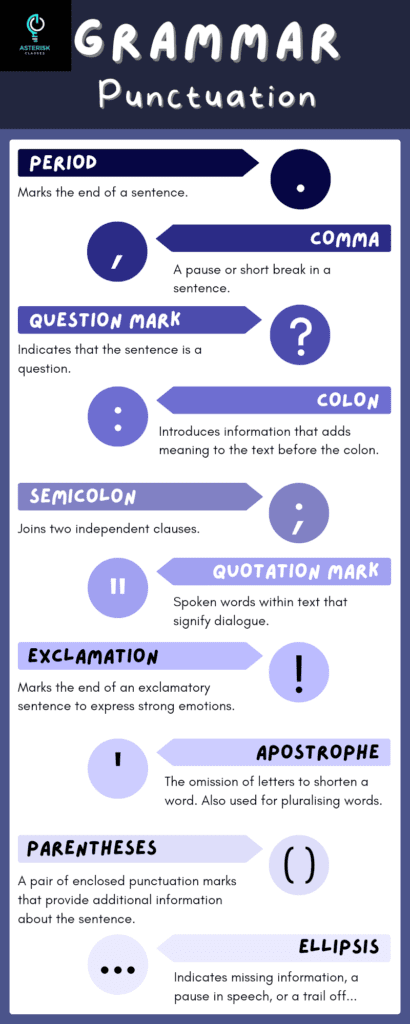
Punctuation refers to the marks used in writing to separate sentences and to clarify meaning. It helps readers understand the structure and flow of written text, indicating pauses, stops, and relationships between different parts of a sentence.
Comma (,)
Uses:
- Separating items in a list: “We need eggs, milk, flour, and sugar.”
- After introductory elements: “Before the meeting, I reviewed the notes.”
- Before conjunctions in compound sentences: “I wanted to go to the park, but it started raining.”
- Setting off non-essential information: “My friend, who is an artist, painted this picture.”
Period (.)
Uses:
- Ending declarative sentences: “She completed her assignment.”
- Abbreviations: “Dr. Smith will see you now.”
Question Mark (?)
Uses:
- Ending direct questions: “What time is the event?”
- Expressing uncertainty or doubt: “Do you think it’s going to rain?”
Exclamation Mark (!)
Uses:
- Ending exclamatory sentences: “That was an incredible performance!”
- Expressing strong emotion or surprise: “I can’t believe you did that!”
Colon (:)
Uses:
- Introducing a list or explanation: “We need the following items: paper, pens, and folders.”
- Introducing a quote: “The sign read: ‘No entry after dark.’”
Semicolon (;)
Uses:
- Connecting closely related independent clauses: “I have a meeting tomorrow; I need to prepare tonight.”
- Separating items in a complex list: “On our trip, we visited New York, New York; Paris, France; and Tokyo, Japan.”
Dash (—)
Uses:
- Indicating a break in thought or additional information: “She was late—again—for the meeting.”
- Setting off a summary or explanation: “He had one major flaw—he was always late.”
Parentheses (())
Uses:
- Enclosing additional information or clarifications: “The concert (which was postponed) has been rescheduled.”
- Indicating asides or afterthoughts: “She called me (the one she met last year) to check in.”
Quotation Marks (” “)
Uses:
- Enclosing direct speech or quotes: “She said, ‘I’ll be there soon.'”
- Highlighting specific words or phrases: “The term ‘sustainable’ is often used in the report.”
Apostrophe (’)
Uses:
- Showing possession: “James’s book” (one book belonging to James), “The cats’ toys” (toys belonging to multiple cats).
- Forming contractions: “Can’t” (cannot), “They’re” (they are).
Ellipsis (…)
Uses:
- Indicating omitted text or trailing off: “I’m not sure what to say…”
- Creating suspense or unfinished thoughts: “She was about to tell him, but then…”
Each punctuation mark plays a crucial role in ensuring clear and effective communication in writing.
