The Most important questions of Gravitation class 9th Science NCERT Solution are as :
Question 1: State the universal law of gravitation?
Answer: The universal law of gravitation states that every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. Mathematically, it is expressed as:
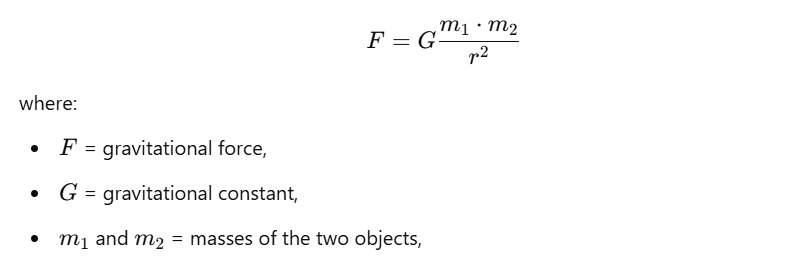
Question 2: Write the formula to find the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface of the earth.
Answer: The formula to find the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on its surface is:

Question 3: What do you mean by free fall?
Answer: Free fall is the motion of an object under the influence of gravitational force only. In free fall, there are no other forces acting on the object, such as air resistance, and it accelerates downwards solely due to gravity.
Question 4: What do you mean by acceleration due to gravity?
Answer: Acceleration due to gravity (ggg) is the rate at which an object accelerates when it is in free fall near the surface of a planet. On Earth, the average value of ggg is approximately 9.8 m/s². This acceleration is caused by the gravitational pull of the Earth.
Question 5: What are the differences between the mass of an object and its weight?
Answer:
- Mass: Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. It is a scalar quantity measured in kilograms (kg) and remains constant regardless of location.
- Weight: Weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. It is a vector quantity measured in newtons (N) and depends on the gravitational field strength. Weight varies with location due to changes in gravitational pull.
Question 6: Why is the weight of an object on the moon 1/6th its weight on the earth?
Answer: The weight of an object on the moon is 1/6th of its weight on Earth because the moon’s gravitational force is about 1/6th as strong as Earth’s. The acceleration due to gravity on the moon is approximately 1.63 m/s², while on Earth, it is about 9.8 m/s². Since weight is directly proportional to gravitational acceleration, the object’s weight on the moon is significantly reduced.
Excercise
Question 1: How does the force of gravitation between two objects change when the distance between them is reduced to half?
Answer: According to the universal law of gravitation, the gravitational force (F) between two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between them. This relationship is expressed as:

Question 2: Gravitational force acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why, then, does a heavy object not fall faster than a light object?
Answer: The acceleration due to gravity (g) is constant for all objects near the surface of the Earth, regardless of their masses. While a heavier object experiences a greater gravitational force because of its larger mass, it also has greater inertia (resistance to change in motion). These two effects cancel each other out, resulting in the same acceleration (g = 9.8 m/sec square for both heavy and light objects), causing them to fall at the same rate in the absence of air resistance.
Question 3: What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface?
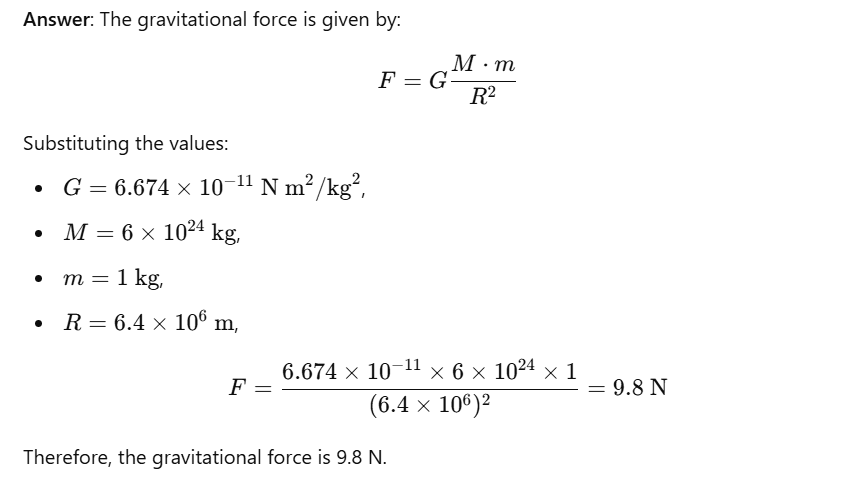
Question 4: The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
Answer: The earth attracts the moon with a force that is equal in magnitude to the force with which the moon attracts the earth. This is due to Newton’s Third Law of Motion, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. Therefore, the gravitational forces are equal and opposite.
Question 5: If the moon attracts the earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon?
Answer: Both the earth and the moon exert gravitational forces on each other, but because the earth’s mass is much larger than the moon’s, the acceleration of the earth towards the moon is negligible compared to the acceleration of the moon towards the earth. This difference in acceleration keeps the earth relatively stationary while the moon orbits the earth.
Question 6: What happens to the force between two objects, if:
(i) The mass of one object is doubled?
Answer: The gravitational force is directly proportional to the product of the masses of the two objects. If the mass of one object is doubled, the gravitational force also doubles.
(ii) The distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
Answer: If the distance is doubled, the force is reduced to 1/4 of its original value, and if the distance is tripled, the force is reduced to 1/9 of its original value, as the force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance.
(iii) The masses of both objects are doubled?
Answer: If the masses of both objects are doubled, the gravitational force becomes four times the original force.
Question 7: What is the importance of the universal law of gravitation?
Answer: The universal law of gravitation explains the motion of celestial bodies and the phenomena of tides. It helps in understanding the structure and dynamics of the universe, including the formation of planets, stars, and galaxies, as well as the behavior of objects on Earth.
Question 8: What is the acceleration of free fall?
Answer: The acceleration of free fall is the acceleration experienced by an object solely due to gravity when no other forces are acting on it. On Earth, this acceleration is approximately 9.8 m/s².
Question 9: What do we call the gravitational force between the earth and an object?
Answer: The gravitational force between the earth and an object is called weight.
Question 10: Amit buys a few grams of gold at the poles as per the instruction of one of his friends. He hands over the same when he meets him at the equator. Will the friend agree with the weight of gold bought? If not, why?
Answer: The friend may not agree with the weight of the gold because the value of g (acceleration due to gravity) is greater at the poles than at the equator. Since weight is the product of mass and g, the weight of the gold will be slightly less at the equator compared to the poles.
Question 11: Why will a sheet of paper fall slower than one that is crumpled into a ball?
Answer: A sheet of paper falls slower than a crumpled one due to air resistance. The flat sheet has a larger surface area and experiences more air resistance, which slows its fall. The crumpled paper has less surface area and experiences less air resistance, allowing it to fall faster.
Question 12: Gravitational force on the surface of the moon is only 1/6 as strong as gravitational force on the earth. What is the weight in newtons of a 10 kg object on the moon and on the earth?
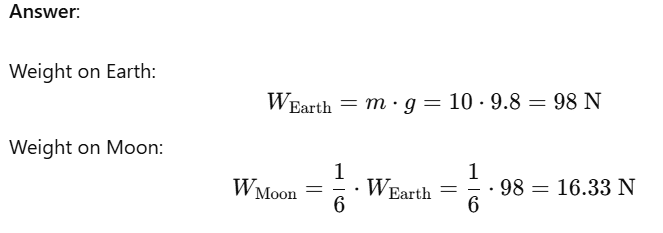
Therefore, the weight of a 10 kg object is 98 N on Earth and approximately 16.33 N on the moon.
Question 13: A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 49 m/s. Calculate
(i) the maximum height to which it rises,
(ii) the total time it takes to return to the surface of the earth.
Answer:
(i) The maximum height (h) is calculated using the formula:
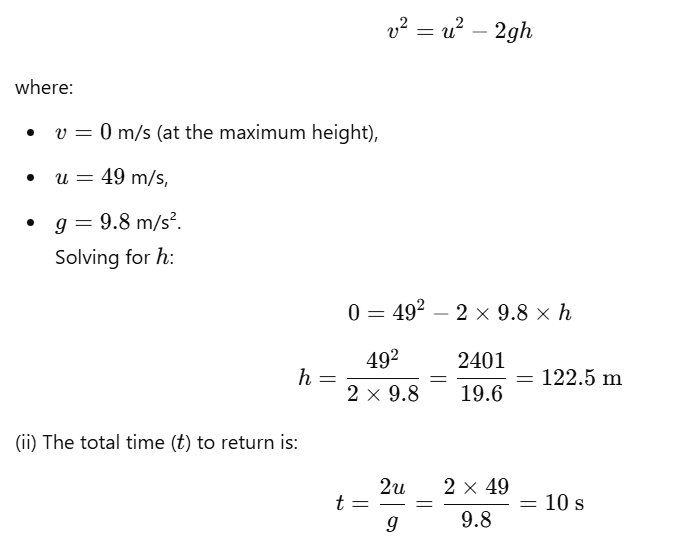
Question 14: A stone is released from the top of a tower of height 19.6 m. Calculate its final velocity just before touching the ground.
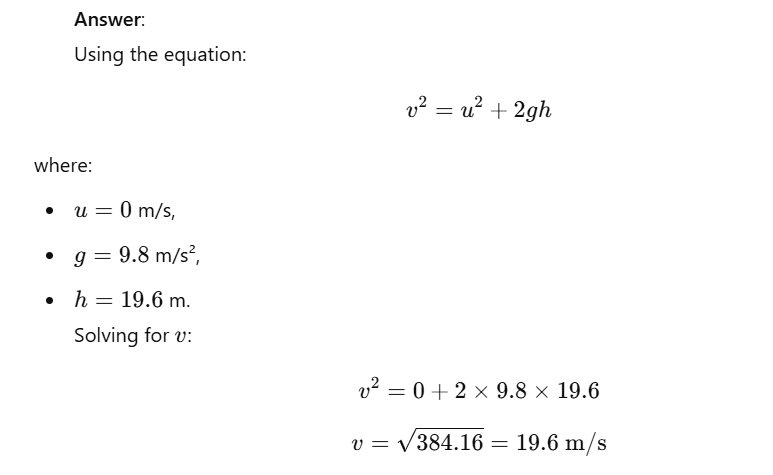
Question 15: A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 40 m/s. Taking g=10 m/s², find the maximum height reached by the stone. What is the net displacement and the total distance covered by the stone?
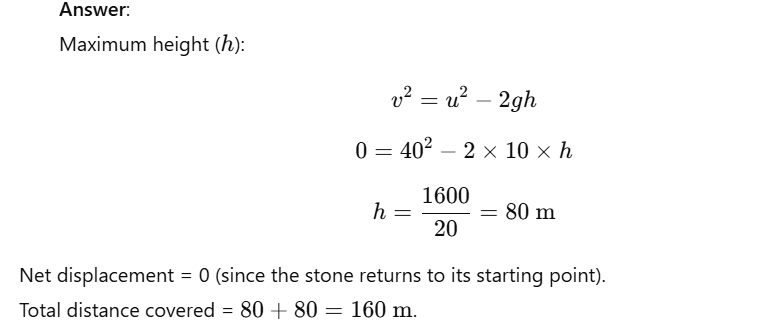
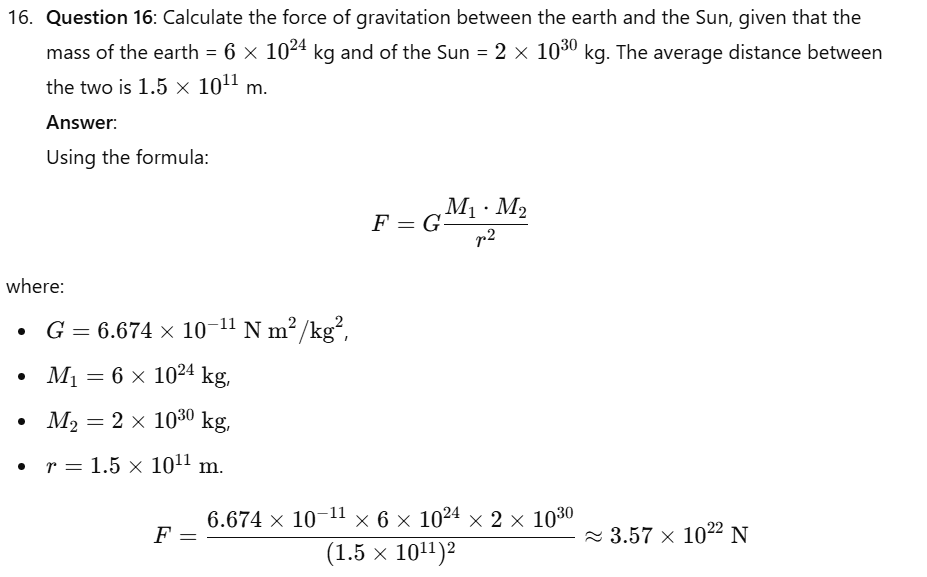
Question 17: A stone is allowed to fall from the top of a tower 100 m high and at the same time another stone is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m/s. Calculate when and where the two stones will meet.
Answer:
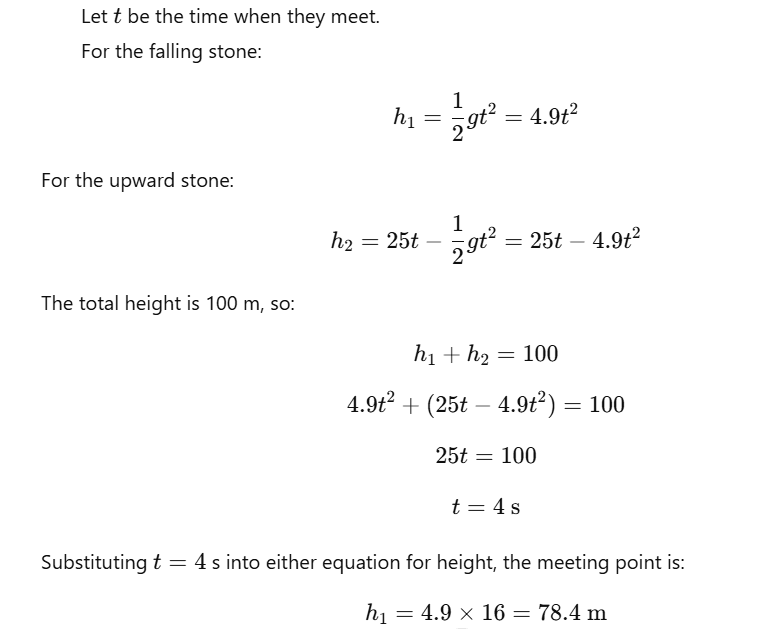
Question 18: A ball thrown up vertically returns to the thrower after 6 s. Find
(a) the velocity with which it was thrown up,
(b) the maximum height it reaches, and
(c) its position after 4 s.

Notes
Introduction to Gravitation
Gravitation is a natural phenomenon by which all things with mass or energy are brought toward one another, including objects ranging from atoms to planets and stars. Sir Isaac Newton formulated the Universal Law of Gravitation.
Universal Law of Gravitation
The Universal Law of Gravitation states that every point mass in the universe attracts every other point mass with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.

Importance of the Universal Law of Gravitation
- Explains Planetary Motion: It helps understand how planets revolve around the sun and satellites around planets.
- Tides: The gravitational force is responsible for the tides in the oceans due to the moon’s pull.
- Formation of Tides and Orbits: It governs the motion of planets and formation of tides.
- Binding Force: It acts as a binding force that keeps the solar system intact.
Free Fall
An object is said to be in free fall if it is falling solely under the influence of gravity, without any air resistance. During free fall, the only force acting on the object is gravitational force.
Acceleration due to Gravity (g):g=9.8 m/s2
Acceleration Due to Gravity
The acceleration experienced by an object when it falls freely under the influence of gravity is called acceleration due to gravity. It is denoted by ggg and varies slightly over the surface of the Earth.
Mass and Weight
- Mass: Mass is the measure of the amount of matter in an object. It is constant and does not change with location.
- Weight: Weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object. It depends on the mass of the object and the acceleration due to gravity.
Weight Formula:W=mg
Where:
- W = Weight
- m = Mass
- g = Acceleration due to gravity
Gravitational Force Between Earth and an Object
The gravitational force between the Earth and an object can be calculated using the formula:

Motion of Planets and Satellites
Planets revolve around the Sun in elliptical orbits due to the gravitational force of the Sun. Similarly, satellites revolve around planets due to the gravitational pull of the planets.
Gravitation and the Moon
The Moon orbits the Earth due to the gravitational force exerted by the Earth. The gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon is mutual and keeps the Moon in its orbit.
Tides
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and the Sun on the Earth. The Moon’s gravitational pull has a greater effect because it is closer to the Earth.
Gravitational Force in Daily Life
- Walking: The gravitational force keeps us grounded.
- Tides: The ocean tides are influenced by the gravitational forces of the Moon and the Sun.
- Weight of Objects: The weight we measure is due to the gravitational force exerted by the Earth.