Current electricity class 12 notes:Electrical Energy & Power
Unit 2 • Current ElectricityUnderstanding energy conversion and power dissipation in electrical circuits
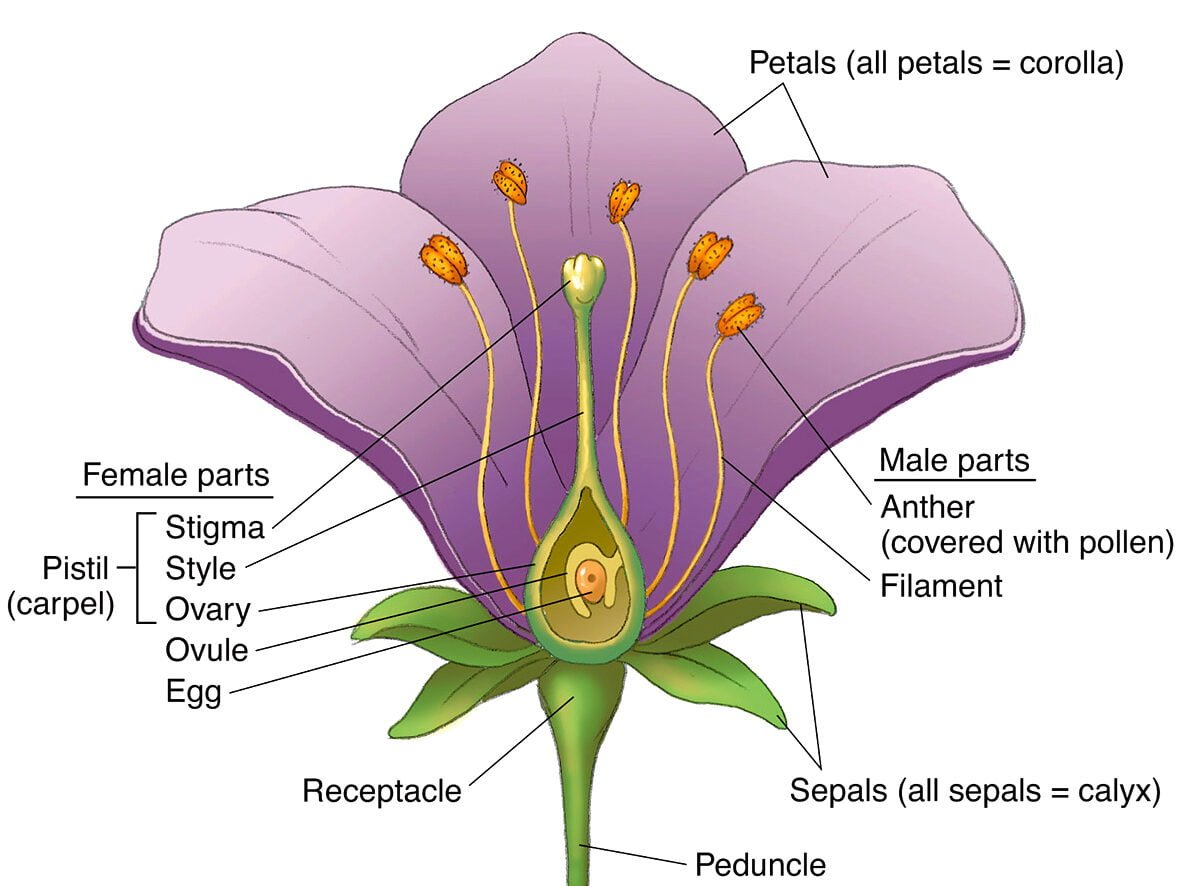
Electrical Energy
Definition:
Electrical energy is the work done by moving electric charges through a potential difference, converting electrical potential energy to other forms (heat, light, mechanical).
Energy Equations
Where:
W = Energy (Joules)
Q = Charge (Coulombs)
V = Potential difference (Volts)
I = Current (Amperes)
t = Time (seconds)
Practical Units
Commercial Unit:
(1 kilowatt-hour = 1000 watts × 3600 seconds)
- 1 Joule = work done when 1A current flows through 1Ω for 1s
- Electricity bills use kWh for energy measurement
- 1 calorie = 4.184 J (for heat energy calculations)
Electrical Power
Definition:
Electrical power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit, measured in Watts (Joules/second).
Power Equations
Power Dissipation
- In resistors: Power is dissipated as heat (Joule heating)
- In motors: Converted to mechanical work + heat
- In LEDs: Converted to light + heat
- Maximum power transfer occurs when Rload = Rsource
Power in Different Configurations
| Circuit Element | Power Formula | Energy Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor | I²R or V²/R | Heat |
| Battery (discharging) | VI | Chemical → Electrical |
| Motor | VI – I²R | Electrical → Mechanical |
| LED | VI | Electrical → Light |
Efficiency & Cost Calculations
Efficiency
Examples:
- Incandescent bulb: ~5% (95% heat)
- LED bulb: ~30% (70% heat)
- Electric motor: 70-95%
- Power lines: ~98%
Energy Cost
Example Calculation:
200W fridge running 24/7 at ₹5/kWh:
Worked Example
Problem:
A 1.5kW electric kettle operates at 220V and takes 10 minutes to boil water. Calculate:
- Current drawn
- Resistance of heating element
- Energy consumed in kWh
- Cost to run 4 times/day at ₹6/kWh
Solution:
(1) Current drawn:
(2) Resistance:
(3) Energy per use:
(4) Daily cost:
Practice Problems
Problem 1
A 100W bulb operates at 220V. Calculate its resistance and current drawn.
Problem 2
Calculate the monthly cost of running a 2kW AC for 8 hours daily at ₹8/kWh.
Problem 3
A motor draws 5A from 220V supply with 85% efficiency. Calculate output power and energy lost in 1 hour.
Problem 4
Compare the cost of running a 60W CFL and 15W LED for 10 years (6h/day) at ₹7/kWh.
Problem 5
A 1Ω resistor carries 5A current for 30 minutes. Calculate heat produced in joules and calories.
Key Takeaways
Essential Formulas
- Energy: W = VIt = I²Rt = V²t/R
- Power: P = VI = I²R = V²/R
- 1 kWh = 3.6×106 J
- 1 cal = 4.184 J
Practical Considerations
- Higher power devices need thicker wires
- Energy efficiency saves money long-term
- Heat dissipation must be managed in circuits
- Power ratings indicate maximum safe operation
Next Topic: Electrical Resistivity & Conductivity
In the next section, we’ll explore the intrinsic properties of materials that determine their resistance to current flow.
Continue to Next Topic →