Dalton’s Atomic Theory Class 12th Chemistry Notes
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
History
Dalton’s atomic theory, proposed by John Dalton in 1808, was the first scientific theory to explain the nature of matter in terms of atoms. Dalton’s work laid the foundation for modern chemistry, and although his theory had limitations, it revolutionized the way scientists understood matter.
Postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory
Dalton’s atomic theory is based on several fundamental postulates:
- All matter is made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass, size, and properties.
- Atoms cannot be created, divided, or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds.
- In a chemical reaction, atoms are rearranged, but their total number remains unchanged.
Examples
Example 1:
Water (H2O) is a compound formed when two hydrogen atoms combine with one oxygen atom in a fixed ratio of 2:1. According to Dalton, this combination follows the postulate that atoms combine in simple whole-number ratios.
Example 2:
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a compound consisting of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. The fixed ratio of 1:2 is consistent with Dalton’s theory.
Limitations of Dalton’s Atomic Theory
Although Dalton’s theory was revolutionary, it had some limitations:
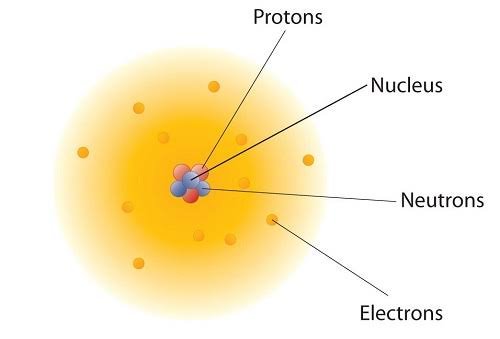
- It assumed that atoms are indivisible, but later discoveries like the electron, proton, and neutron showed that atoms are made of smaller subatomic particles.
- Dalton stated that atoms of a given element are identical, but isotopes of the same element have different masses.
- The theory could not explain the existence of allotropes (e.g., carbon exists as both graphite and diamond).