Difference Between Inductive Effect and Electromeric Effect
Understand key organic effects, their mechanisms, and their role in chemical reactions — a must-know for NEET, JEE, and CBSE exams.
Introduction
In organic chemistry, electronic effects profoundly influence the reactivity, stability, and acidity of compounds. Among these, Inductive Effect and Electromeric Effect are two crucial mechanisms. This article aims to dissect their differences, mechanisms, and significance in a clear and exhaustive manner.
What is Inductive Effect?
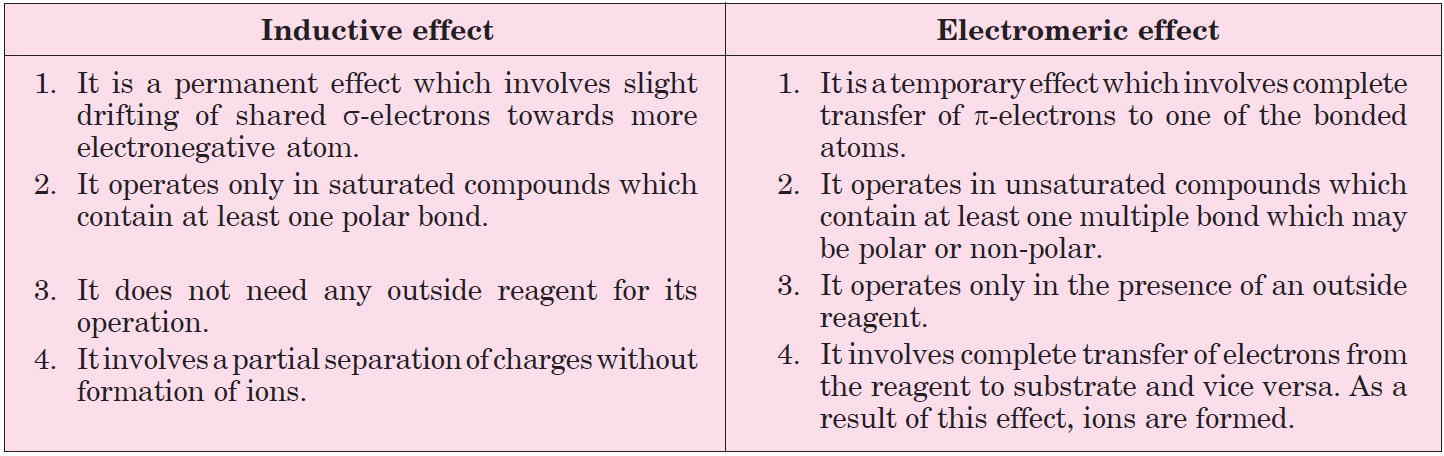
Inductive Effect refers to the permanent electron displacement along a sigma bond due to electronegativity differences between two atoms. This happens when an electronegative atom pulls electron density toward itself.
Key Characteristics
- Permanent
- Distance-dependent (diminishes with distance)
- Transmitted through sigma bonds
- Controlled by electronegativity
➥ Example: Cl-CH₂-CH₃ — Cl is electronegative, it pulls electron density toward it, causing a -I (negative) inductive effect.
What is Electromeric Effect?
Electromeric Effect involves a temporary redistribution of electron pairs in a multiple bond (typically a double bond) in response to an external attack by a reagent. This happens instantaneously during a reaction.
Key Characteristics
- Temporary
- Completely reversible after attack
- Operates through pi-electron pairs
- Initiated by an electrophile or nucleophile
➥ Example: In the attack of a proton (H+) on an alkene, the pi-electron pair is completely shifted toward the proton.
Key Difference Between Inductive and Electromeric Effect
- Inductive is permanent; Electromeric is temporary.
- Inductive operates through sigma bonds; Electromeric operates through pi bonds.
- Inductive is influenced by electronegativity; Electromeric is influenced by attack by electrophile or nucleophile.
- Inductive effects diminish with distance; Electromeric effects are concentrated at reactive sites.
✅ Always remember: Inductive = permanent, sigma; Electromeric = temporary, pi.
FAQs About Difference Between Inductive Effect and Electromeric Effect
- What is inductive effect? — It’s the permanent electron displacement due to electronegativity.
- What is electromeric effect? — It’s the temporary electron redistribution in a multiple bond under attack.
- Is inductive permanent or temporary? — It’s permanent.
- Is electromeric permanent or temporary? — It’s temporary.
- Through which bonds does inductive operate? — Sigma bonds.
- Through which bonds does electromeric operate? — Pi bonds.
- What kind of groups show +I or -I effects? — Electron-donating (+I) or electron-withdrawing (-I) groups.
- What kind of attack stimulates electromeric effects? — Electrophilophytic or nucleophilophytic attack.
- Where is inductive most pronounced? — Closer to the electronegative atom; it weakens with distance.
- Where is electromeric most pronounced? — At the reactive multiple bond (alkene, alkyne, carbonyl, etc.).
Summary
In a nutshell, the inductive effect involves a permanent redistribution of electron density due to electronegativity, while the electromeric effect involves a temporary redistribution upon attack by a reagent. Both mechanisms profoundly influence the reactivity and stability of organic compounds.
✨ If you found this helpful, please share your thoughts in the comments or check out our related posts for more in-depth explanations on organic effects in NEET and JEE exams.