Electric Generator (Dynamo)
What is an Electric Generator?
An electric generator, also known as a dynamo, is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction and is widely used to generate electricity in power plants, vehicles, and portable devices.
Construction of an Electric Generator
An electric generator consists of the following main components:
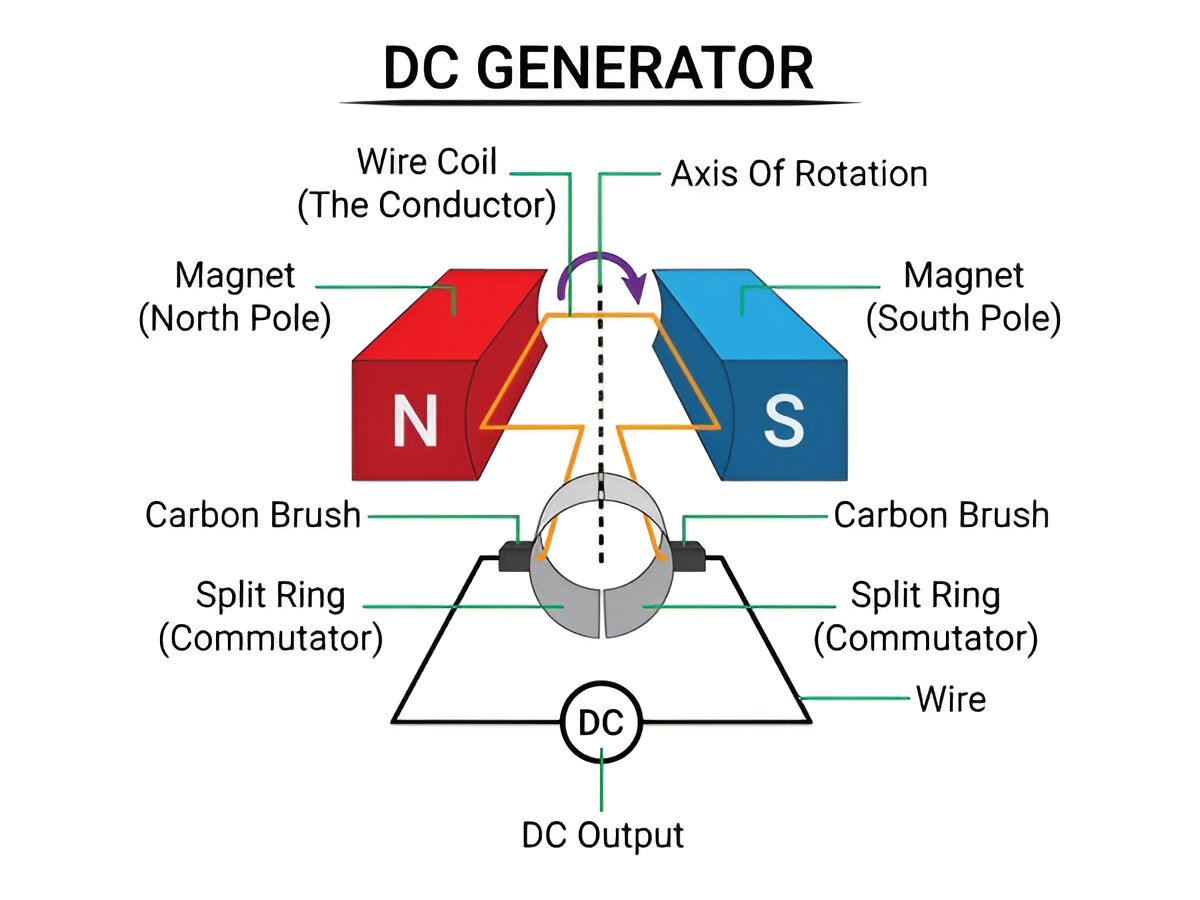
- Armature: A coil of insulated copper wire that rotates in a magnetic field.
- Magnetic Field: Provided by permanent magnets or electromagnets.
- Slip Rings: Conductors that allow the transfer of current from the rotating coil to the external circuit.
- Brushes: Carbon brushes that maintain contact with the slip rings.
- Axle: The rotating shaft connected to the armature.
Construction of an Electric Generator
Principle of an Electric Generator
An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which states that a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor. The induced EMF is given by:
Where:
- EMF = Electromotive force (in Volts).
- N = Number of turns in the coil.
- dΦ/dt = Rate of change of magnetic flux (in Weber/second).
Working of an Electric Generator
The working of an electric generator can be explained in the following steps:
- The armature coil rotates in a magnetic field, causing a change in magnetic flux.
- According to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, an EMF is induced in the coil.
- The slip rings and brushes transfer the induced current to the external circuit.
- The direction of the induced current changes every half rotation, producing alternating current (AC).
Working of an Electric Generator

Functions of an Electric Generator
The primary functions of an electric generator are:
- To convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- To produce alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) depending on the design.
- To provide a reliable source of electricity in power plants, vehicles, and portable devices.
Applications of Electric Generators
Electric generators are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Power Plants: To generate electricity from coal, hydro, nuclear, or wind energy.
- Vehicles: In alternators to charge batteries and power electrical systems.
- Portable Generators: For backup power during outages or in remote locations.
- Renewable Energy: In wind turbines and solar power systems.
Types of Electric Generators
Electric generators are classified into two main types:
- AC Generators: Produce alternating current (AC). Examples include synchronous and induction generators.
- DC Generators: Produce direct current (DC). Examples include shunt, series, and compound generators.
Types of Electric Generators

Differences Between Electric Motor and Generator
The key differences between an electric motor and an electric generator are:
| Aspect | Electric Motor | Electric Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. | Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. |
| Principle | Magnetic effect of electric current. | Electromagnetic induction. |
| Input | Electrical energy. | Mechanical energy. |
| Output | Mechanical energy (rotation). | Electrical energy (current). |
| Applications | Fans, washing machines, electric vehicles, etc. | Power plants, alternators, portable generators, etc. |
Key Points to Remember
- An electric generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
- The two main types of generators are AC generators and DC generators.
- Electric generators are used in power plants, vehicles, and portable devices.
- The key difference between a motor and a generator is their function: a motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, while a generator does the opposite.