Electric Motor
What is an Electric Motor?
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. It works on the principle of the magnetic effect of electric current and is widely used in various applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Construction of an Electric Motor
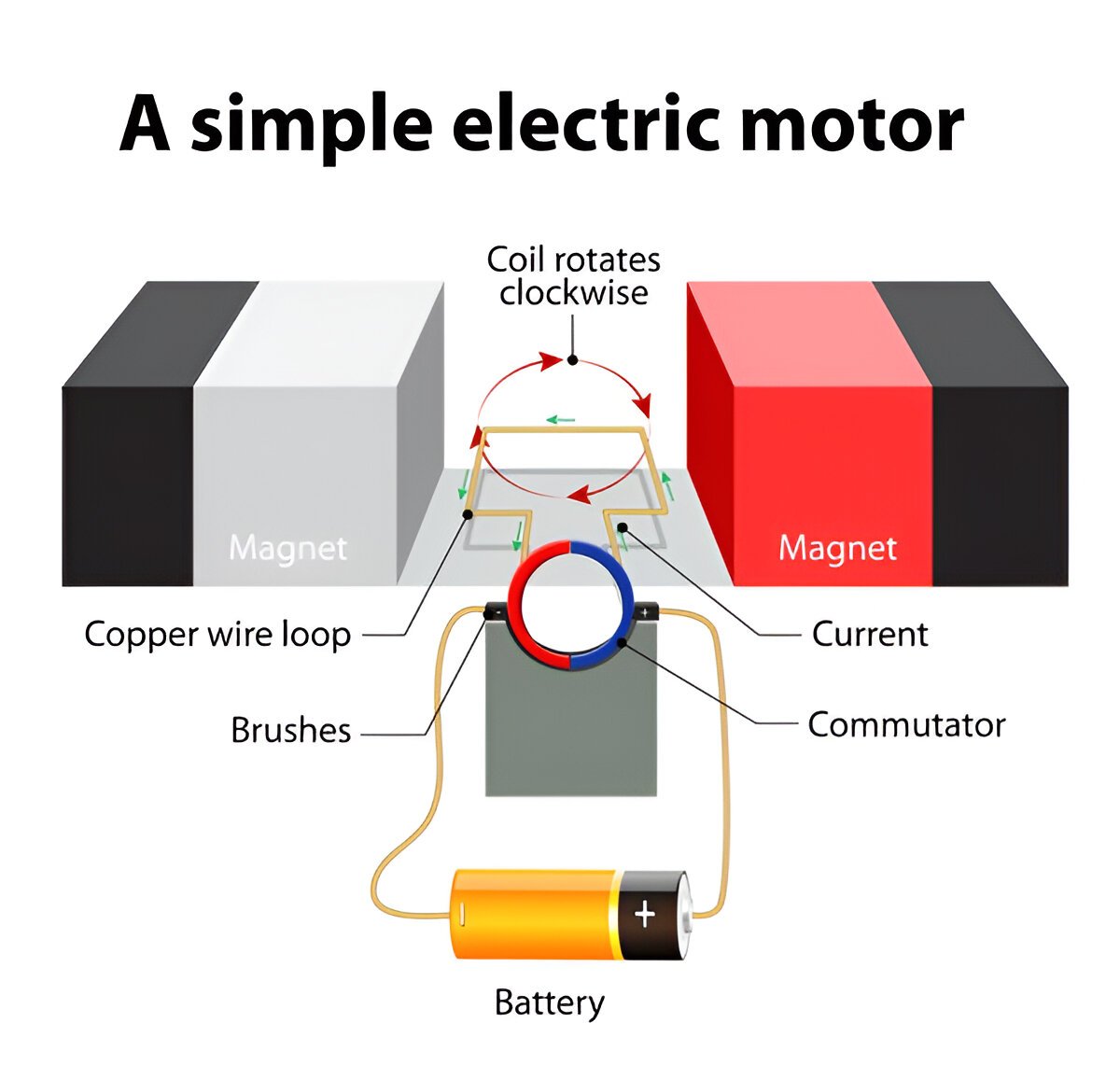
An electric motor consists of the following main components:
- Armature: A rectangular coil of insulated copper wire placed between the poles of a magnet.
- Magnetic Field: Provided by permanent magnets or electromagnets.
- Commutator: A split ring that reverses the direction of current in the armature coil.
- Brushes: Carbon brushes that supply current to the commutator.
- Axle: The rotating shaft connected to the armature.
Construction of an Electric Motor

Principle of an Electric Motor
An electric motor works on the principle that a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field experiences a force. The direction of the force is given by Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule.
Where:
- F = Force on the conductor (in Newtons).
- I = Current in the conductor (in Amperes).
- L = Length of the conductor (in meters).
- B = Magnetic field strength (in Tesla).
- θ = Angle between the current direction and the magnetic field.
Working of an Electric Motor
The working of an electric motor can be explained in the following steps:
- When current flows through the armature coil, it experiences a force due to the magnetic field.
- The commutator reverses the direction of current in the coil every half rotation, ensuring continuous rotation.
- The armature rotates, and the axle connected to it performs mechanical work.
Working of an Electric Motor
Functions of an Electric Motor
The primary functions of an electric motor are:
- To convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- To produce rotational motion for driving machines and appliances.
- To provide precise control over speed and torque.
Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Household Appliances: Fans, washing machines, refrigerators, etc.
- Industrial Machinery: Conveyor belts, pumps, compressors, etc.
- Transportation: Electric vehicles, trains, and elevators.
- Robotics: Precision control in robotic arms and drones.
Types of Electric Motors
Electric motors are classified into two main types:
- DC Motors: Operate on direct current (DC). Examples include brushed and brushless DC motors.
- AC Motors: Operate on alternating current (AC). Examples include induction motors and synchronous motors.
Types of Electric Motors

Key Points to Remember
- An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- It works on the principle of the magnetic effect of electric current.
- The direction of the force is given by Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule.
- Electric motors are used in household appliances, industrial machinery, transportation, and robotics.
- The two main types of electric motors are DC motors and AC motors.