Emperical Formula and Molecular Formula
Empirical and Molecular Formulas
Empirical formula of a compound is the formula written with the simplest ratio of the number of different atoms present in one molecule of the compound as a subscript to the atomic symbol.
Molecular formula is the formula written with the actual number of different atoms present in one molecule as a subscript to the atomic symbol.
1.6.1 Determination of Empirical Formula from Elemental Analysis Data:
Step 1:
Since the composition is expressed in percentage, we can consider the total mass of the compound as 100 g and the percentage values of individual elements as mass in grams.
Step 2:
Divide the mass of each element by its atomic mass. This gives the relative number of moles of various elements in the compound.
Step 3:
Divide the value of relative number of moles obtained in Step 2 by the smallest number of them to get the simplest ratio.
Step 4:
(Only if necessary) In case the simplest ratios obtained in Step 3 are not whole numbers, they may be converted into whole numbers by multiplying by a suitable smallest number.
Example:
An acid found in tamarind on analysis shows the following percentage composition: 32% Carbon; 4% Hydrogen; 64% Oxygen. Find the empirical formula of the compound.
| Element | Percentage | Molar Mass | Relative No. of Moles | Simplest Ratio | Simplest Ratio (Whole No.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 32 | 12 | 2.66 | 2.66 / 1.5 = 1.77 | 2 |
| H | 4 | 1 | 4 | 4 / 1.5 = 2.67 | 3 |
| O | 64 | 16 | 4 | 4 / 1.5 = 2.67 | 3 |
Empirical formula: C2H3O3
1.6.2 Calculation of Molecular Formula from Empirical Formula:
The molecular formula is a whole-number multiple of the empirical formula. The whole number can be calculated using the formula:
Whole number (n) =
Calculated empirical formula mass
Example:
Formula for the compound present in vinegar:
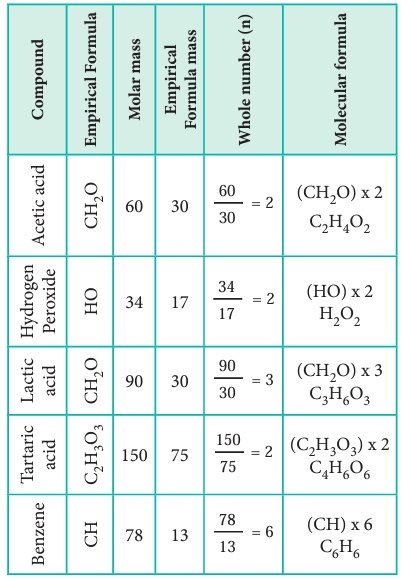
| Compound | Empirical Formula | Molar Mass | Empirical Formula Mass | Whole Number (n) | Molecular Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetic acid | CH2O | 60 | 30 | 2 | C2H4O2 |
| Lactic acid | CH2O | 90 | 30 | 3 | C3H6O3 |
Two organic compounds present in vinegar (molar mass: 60 g/mol) and sour milk (molar mass: 90 g/mol) have the following percentage composition: C – 40%, H – 6.6%, O – 53.4%. Find their molecular formulas.
Solution:
Both compounds have the same mass percentage composition. Therefore, their empirical formula is CH2O.
Empirical formula mass (CH2O) = 12 + (2 × 1) + 16 = 30 g/mol
Formula for the compound present in vinegar: Molecular formula = (CH2O) × 2 = C2H4O2
Formula for the compound present in sour milk: Molecular formula = (CH2O) × 3 = C3H6O3
Evaluate Yourself:
-
Experimental analysis of a compound containing the elements x, y, z gives the following data: x = 32%, y = 24%, z = 44%. The relative number of atoms of x, y, and z are 2, 1, and 0.5, respectively. (Molecular mass = 400 g/mol). Determine:
- i) The atomic masses of the elements x, y, z.
- ii) The empirical formula of the compound.
- iii) The molecular formula of the compound.