Human Eye: Structure and Functions
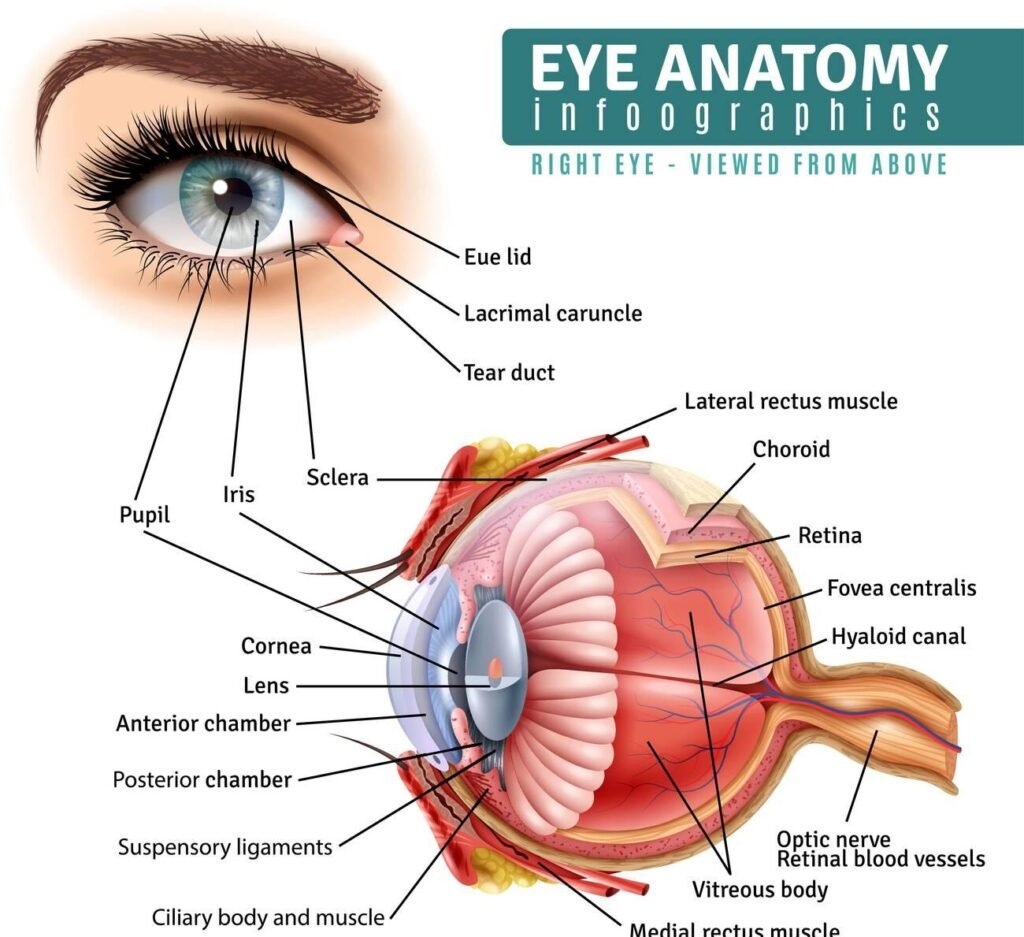
Cornea
Function: The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. It refracts light and helps focus light onto the retina.
Unique Fact: The cornea is the only tissue in the human body that doesn’t contain blood vessels.
Iris
Function: The iris is the colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil and thus the amount of light that enters the eye.
Unique Fact: The color of the iris is determined by the amount and type of pigments in the iris tissue.
Pupil
Function: The pupil is the black circular opening in the center of the iris that allows light to enter the eye and reach the retina.
Unique Fact: The pupil dilates (expands) in low light and constricts (shrinks) in bright light to regulate the amount of light entering the eye.
Lens
Function: The lens is a transparent, flexible structure located behind the iris. It focuses light onto the retina by changing its shape.
Unique Fact: The lens becomes less flexible with age, leading to a condition called presbyopia, which makes it harder to focus on close objects.
Retina
Function: The retina is the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye. It converts light into electrical signals that are sent to the brain via the optic nerve.
Unique Fact: The retina contains two types of photoreceptor cells: rods (for low-light vision) and cones (for color vision).
Optic Nerve
Function: The optic nerve transmits visual information from the retina to the brain.
Unique Fact: The optic nerve is composed of over a million nerve fibers, making it one of the most complex nerves in the human body.
Sclera
Function: The sclera is the white outer layer of the eye. It provides structural support and protection to the inner parts of the eye.
Unique Fact: The sclera is made up of tough, fibrous tissue that helps maintain the shape of the eye.
Choroid
Function: The choroid is a layer of blood vessels located between the retina and the sclera. It supplies nutrients and oxygen to the retina.
Unique Fact: The choroid contains a high concentration of melanin, which helps absorb excess light and prevent reflection within the eye.
Ciliary Body
Function: The ciliary body is a ring-shaped tissue that produces the aqueous humor and controls the shape of the lens.
Unique Fact: The ciliary body contains muscles that contract and relax to change the shape of the lens, a process known as accommodation.
Vitreous Humor
Function: The vitreous humor is a clear, gel-like substance that fills the space between the lens and the retina. It helps maintain the shape of the eye and transmits light to the retina.
Unique Fact: The vitreous humor is 99% water, but it also contains collagen and hyaluronic acid, which give it a gel-like consistency.
Unique Facts About the Human Eye
- The human eye can distinguish about 10 million different colors.
- Your eyes can process 36,000 bits of information every hour.
- The eye is the second most complex organ in the body, after the brain.
- Blinking helps to keep the eye moist and free of dust and debris.
- The eye’s lens is faster than any camera lens, adjusting focus almost instantly.