JKBOSE Class 12 Chemistry Guess paper 2025 syllabus and the unit-wise weightage, here’s a guess paper for the upcoming exam. This guess paper is designed to cover high-weightage topics and frequently asked questions.
JKBOSE Class 12 Chemistry Guess paper 2025
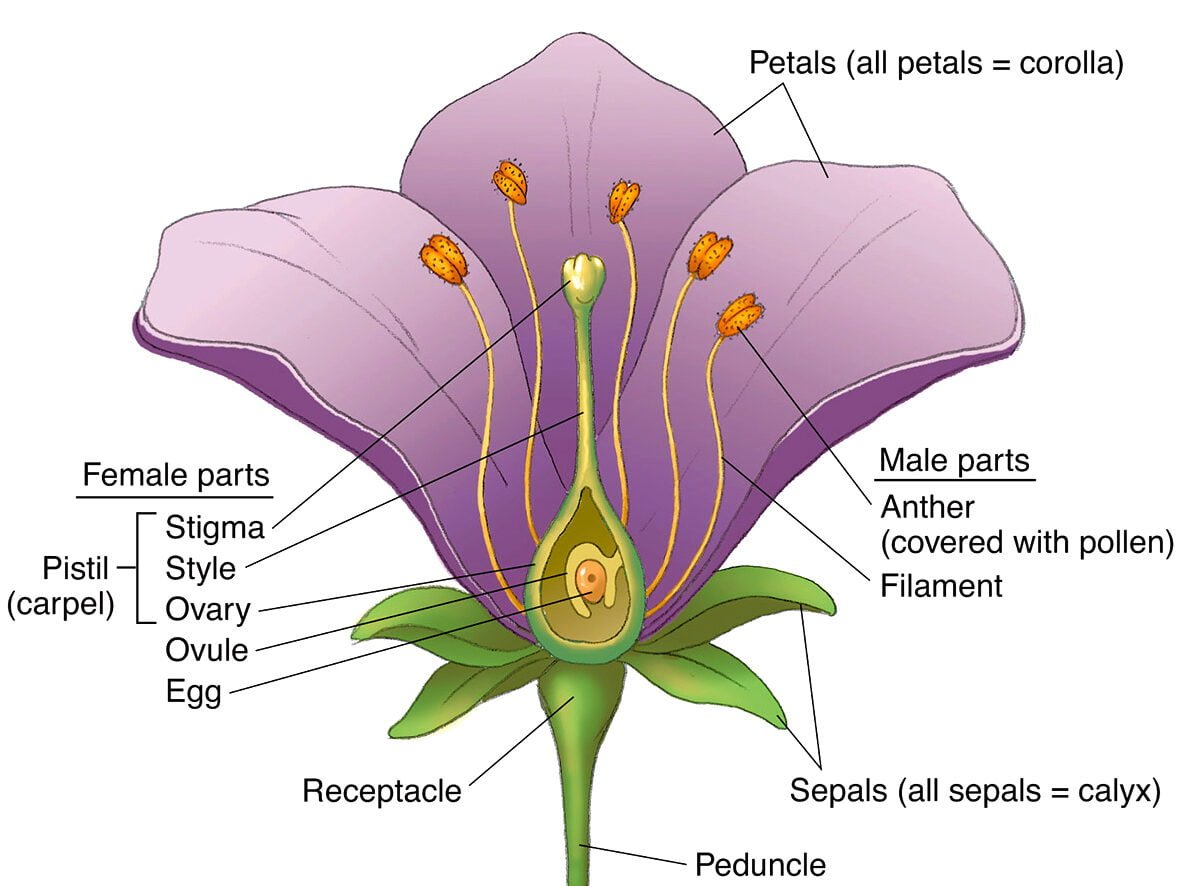
Unit-I: SOLUTIONS (7 Marks)
- Very Short Answer (1 mark)
- Define colligative properties.
- What is Van’t Hoff factor?
- Short Answer I (2 marks)
- Derive the expression for relative lowering of vapor pressure.
- Calculate the molecular mass of a solute if the osmotic pressure of its solution is given.
- Long Answer (4 marks)
- Explain Raoult’s law and its limitations. Derive the expression for elevation in boiling point.
Unit-II: ELECTROCHEMISTRY (9 Marks)
- Very Short Answer (1 mark)
- What is the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)?
- Define molar conductivity.
- Short Answer I (2 marks)
- State Kohlrausch’s law of independent migration of ions.
- Write the Nernst equation and explain its terms.
- Short Answer II (3 marks)
- Explain the working of a lead-acid battery with a diagram.
- Calculate the emf of a cell using the Nernst equation.
- Long Answer (5 marks)
- Derive the relationship between Gibbs energy change and emf of a cell. Discuss the applications of fuel cells.
Unit-III: CHEMICAL KINETICS (7 Marks)
- Very Short Answer (1 mark)
- Define the rate of reaction.
- What is the half-life period of a reaction?
- Short Answer I (2 marks)
- Derive the integrated rate equation for a first-order reaction.
- Explain the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction using the Arrhenius equation.
- Long Answer (4 marks)
- Discuss the collision theory of chemical reactions. Derive the expression for the rate constant of a zero-order reaction.
Unit-IV: d and f-BLOCK ELEMENTS (7 Marks)
- Very Short Answer (1 mark)
- What is lanthanide contraction?
- Why are transition metals good catalysts?
- Short Answer I (2 marks)
- Explain the preparation of K₂Cr₂O₇ from chromite ore.
- Discuss the magnetic properties of transition metals.
- Long Answer (4 marks)
- Compare the properties of lanthanides and actinides. Explain the catalytic properties of transition metals.
Unit-V: CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS (7 Marks)
- Very Short Answer (1 mark)
- What is a ligand? Give an example.
- Define coordination number.
- Short Answer I (2 marks)
- Explain Werner’s theory of coordination compounds.
- Write the IUPAC name of [Co(NH₃)₆]Cl₃.
- Long Answer (4 marks)
- Discuss the bonding in coordination compounds using Valence Bond Theory (VBT). Explain the importance of coordination compounds in biological systems.
Unit-VI: HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES (6 Marks)
- Very Short Answer (1 mark)
- What is the nature of the C-X bond in haloalkanes?
- Give the structure of iodoform.
- Short Answer I (2 marks)
- Explain the mechanism of SN2 reaction in haloalkanes.
- Discuss the environmental effects of DDT.
- Long Answer (3 marks)
- Compare the reactivity of haloalkanes and haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Unit-VII: ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS (6 Marks)
- Very Short Answer (1 mark)
- What is the acidic nature of phenol?
- Give the structure of methanol.
- Short Answer I (2 marks)
- Explain the mechanism of dehydration of alcohols.
- Discuss the electrophilic substitution reactions of phenol.
- Long Answer (3 marks)
- Compare the physical and chemical properties of alcohols and phenols.
Unit-VIII: ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS (8 Marks)
- Very Short Answer (1 mark)
- What is the reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes?
- Give the structure of acetic acid.
- Short Answer I (2 marks)
- Explain the nucleophilic addition reaction in carbonyl compounds.
- Discuss the Hell-Volhard-Zelinskii reaction.
- Long Answer (5 marks)
- Compare the physical and chemical properties of aldehydes and ketones. Explain the mechanism of aldol condensation.
Unit-IX: ORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN (6 Marks)
- Very Short Answer (1 mark)
- What is diazotization?
- Give the structure of aniline.
- Short Answer I (2 marks)
- Explain the Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
- Discuss the basicity of amines.
- Long Answer (3 marks)
- Compare the physical and chemical properties of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines.
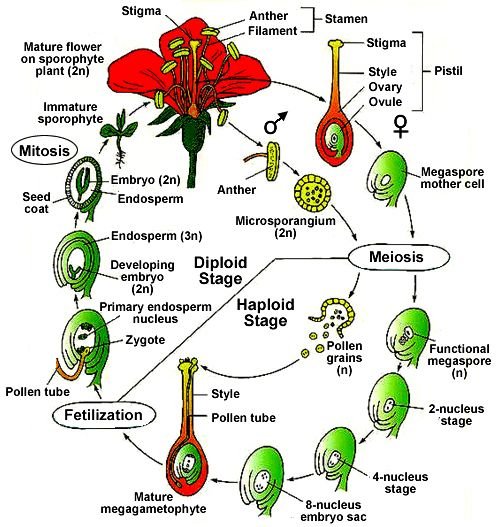
Unit-X: BIOMOLECULES (7 Marks)
- Very Short Answer (1 mark)
- What are reducing sugars?
- Define denaturation of proteins.
- Short Answer I (2 marks)
- Explain the structure of glucose.
- Discuss the functions of nucleic acids.
- Long Answer (4 marks)
- Compare the structures of DNA and RNA. Explain the importance of vitamins in the human body.
Tips for Preparation
- Focus on NCERT: All questions are based on NCERT concepts.
- Practice Numericals: Especially from Solutions, Electrochemistry, and Chemical Kinetics.
- Revise Named Reactions: Mechanisms and distinguishing tests.
- Memorize Structures: Biomolecules (glucose, DNA), coordination geometries.
Important Naming Reactions – Class 12 (JKBOSE)
Equation: 2C6H5CHO + NaOH → C6H5CH2OH + C6H5COONa
Explanation: Aldehydes without α-hydrogen undergo self-oxidation and reduction in the presence of a strong base.
Equation: RCOR’ + Zn(Hg) + HCl → RCH2R’ + ZnCl2
Explanation: This reaction reduces ketones and aldehydes to alkanes using zinc amalgam and concentrated HCl.
Equation: RCOR’ + NH2NH2 + KOH → RCH2R’ + N2
Explanation: Carbonyl compounds are reduced to hydrocarbons using hydrazine and a strong base.
Equation: C6H6 + RCl + AlCl3 → C6H5R + HCl
Explanation: An alkyl group is added to benzene using an alkyl halide in the presence of AlCl3.
Equation: C6H5OH + CHCl3 + NaOH → o-HO-C6H4-CHO + HCl
Explanation: Phenol reacts with chloroform and NaOH to form salicylaldehyde.
Equation: 2CH3CHO → CH3CH(OH)CH=CH2
Explanation: Aldehydes and ketones with α-hydrogen undergo condensation in base to form β-hydroxy aldehydes or ketones.
Equation: C6H5CHO + CH3COOCH3 → C6H5CH=CHCOOH
Explanation: Aldehydes react with acid anhydrides to form α,β-unsaturated acids.
Equation: C6H5Cl + Na + C6H5Cl → C6H5-C6H5 + NaCl
Explanation: Aryl halides react with sodium metal to form biaryl compounds.
Equation: C6H5N2Cl + CuCl → C6H5Cl + N2
Explanation: Aromatic diazonium salts react with CuCl or CuBr to form aryl halides.
Equation: C6H5ONa + CO2 → C6H4(OH)COOH
Explanation: Phenol reacts with CO2 in the presence of NaOH to form salicylic acid.
Additional Naming Reactions – Class 12 (JKBOSE)
Equation: CH3COOH + Br2 + P → CH2BrCOOH + HBr
Explanation: Carboxylic acids with α-hydrogen react with bromine in the presence of phosphorus to form α-bromo acids.
Equation: C6H6 + CO + HCl → C6H5CHO
Explanation: Benzene reacts with CO and HCl in the presence of AlCl3 and CuCl to form benzaldehyde.
Equation: RCOCl + H2 + Pd/BaSO4 → RCHO + HCl
Explanation: Acid chlorides are reduced to aldehydes using hydrogen in the presence of palladium catalyst.
Equation: C6H5CH3 + CrO2Cl2 → C6H5CHO
Explanation: Toluene is oxidized to benzaldehyde using chromyl chloride.
Equation: RCN + SnCl2 + HCl → RCH=NH → RCHO
Explanation: Nitriles are reduced to aldehydes using SnCl2 and HCl.
Equation: RCl + 2Na + R’Cl → R-R’ + 2NaCl
Explanation: Alkyl halides react with sodium metal in dry ether to form higher alkanes.
Equation: R2CuLi + R’X → R-R’ + RCu + LiX
Explanation: Alkyl halides react with lithium dialkylcuprates to form higher alkanes.
Equation: RCl + NaI → RI + NaCl
Explanation: Alkyl chlorides and bromides are converted to alkyl iodides using sodium iodide in acetone.
Equation: C6H5N2Cl → C6H5F + N2 + Cl2
Explanation: Aromatic diazonium salts are converted to aryl fluorides using fluoroboric acid.
Equation: Phthalimide + KOH + R-X → R-NH2
Explanation: Primary amines are synthesized from alkyl halides via phthalimide.