Introduction to Microbes
Microbes, or microorganisms, are tiny living organisms that can be seen only with the help of a microscope. They are found almost everywhere on Earth and play a crucial role in our lives, often in ways we don’t even realize. This blog post will introduce you to different types of microbes, their roles, and their importance in various fields.
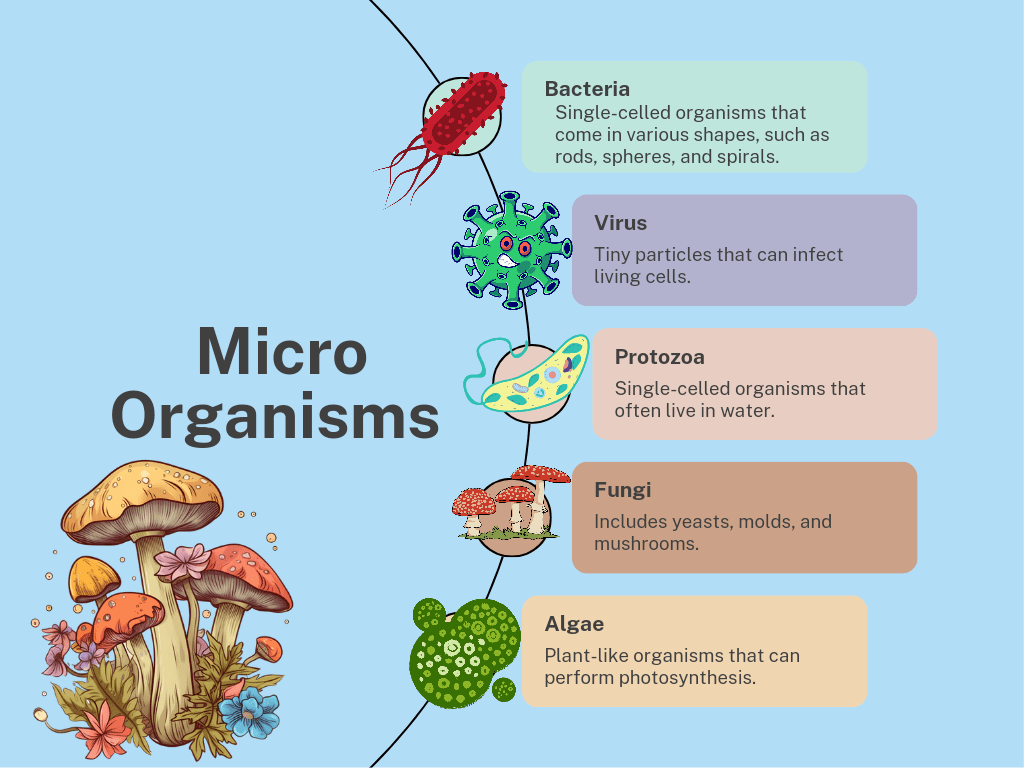
Types of Microbes
There are several types of microbes, including:
- Bacteria: Single-celled organisms that come in various shapes, such as rods, spheres, and spirals. They can live in almost any environment. Example: Escherichia coli, commonly found in the intestines of humans and animals.
- Viruses: Tiny particles that can infect living cells. They need a host to reproduce and can cause diseases. Example: Influenza virus, which causes the flu.
- Fungi: Includes yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. They can be single-celled or multicellular. Example: Penicillium, a mold used to produce the antibiotic penicillin.
- Protozoa: Single-celled organisms that often live in water. They can be free-living or parasitic. Example: Amoeba, which can cause amoebic dysentery.
- Algae: Plant-like organisms that can perform photosynthesis. They are usually found in water. Example: Chlorella, a type of green algae.
Introduction to Viruses
Viruses are unique because they are not considered fully alive. They are made up of genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protein coat. Viruses infect host cells and use the host’s machinery to reproduce. This can often damage or kill the host cell, leading to disease.
Example: HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus), which causes AIDS.
Where Do Microbes Live?
Microbes are incredibly versatile and can live in a wide range of environments:
- Soil: Many bacteria and fungi help decompose organic matter.
- Water: Algae and protozoa are common in both freshwater and marine environments.
- Air: Bacteria and viruses can be airborne and travel long distances.
- Extreme Environments: Some bacteria, known as extremophiles, thrive in extreme conditions like hot springs, deep ocean vents, and acidic environments.
Commercial Use of Microbes
Microbes have numerous commercial applications:
- Fermentation: Bacteria and yeasts are used to make foods and beverages like yogurt, cheese, bread, and beer.
- Biotechnology: Microbes are used to produce enzymes, biofuels, and biodegradable plastics.
- Agriculture: Certain bacteria and fungi are used in biofertilizers to enhance soil fertility.
Medicinal Use of Microbes
Microbes have been used in medicine for centuries:
- Antibiotics: Many antibiotics, like penicillin, are derived from fungi and bacteria.
- Probiotics: Beneficial bacteria that help maintain a healthy gut flora.
- Vaccines: Some vaccines use weakened or killed microbes to stimulate an immune response.
Vaccines
Vaccines are biological preparations that provide immunity to a specific disease. They often contain an agent resembling a disease-causing microbe and help the immune system recognize and fight the microbe if encountered in the future.
Example: The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine.
Microbes’ Role in Increasing Soil Fertility
Microbes play a crucial role in maintaining soil health:
- Nitrogen Fixation: Certain bacteria, like Rhizobium, convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms that plants can use.
- Decomposition: Fungi and bacteria break down organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the soil.
Pathogens
Pathogens are microbes that cause disease. They can infect humans, animals, and plants, leading to various health problems.
Disease-Causing Microorganisms in Humans
Many microbes can cause diseases in humans:
- Bacteria: Tuberculosis (caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis)
- Viruses: Common cold (caused by rhinoviruses)
- Fungi: Athlete’s foot (caused by Trichophyton fungi)
- Protozoa: Malaria (caused by Plasmodium species)
Disease-Causing Microorganisms in Plants
Plants can also be affected by microbial diseases:
- Bacteria: Fire blight (caused by Erwinia amylovora)
- Viruses: Tobacco mosaic virus
- Fungi: Rusts (caused by Puccinia species)
Disease-Causing Microorganisms in Animals
Animals can suffer from microbial infections as well:
- Bacteria: Anthrax (caused by Bacillus anthracis)
- Viruses: Rabies (caused by the rabies virus)
- Fungi: Ringworm (caused by various fungal species)
Food Preservation
Microbes can spoil food, but we can use various methods to prevent this:
- Refrigeration: Slows down microbial growth.
- Canning: Kills microbes through heat.
- Drying: Removes water, which microbes need to grow.
- Salting: Creates an environment with high osmotic pressure that inhibits microbial growth.
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a process where certain bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, a form that plants can absorb and use. This process is crucial for plant growth and agriculture.
Example: Rhizobium bacteria, which live in the root nodules of leguminous plants.
Understanding these basic concepts about microbes can help you appreciate their importance in our world and their impact on various aspects of life and industry.
Textual Questions and answers
Fill in the Blanks
Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a __.
- Microscope
Blue-green algae fix __ directly from air and enhance the fertility of the soil.
- Nitrogen
Alcohol is produced with the help of __.
- Yeast
Cholera is caused by __.
- Bacteria
True or False
Yeast is used in the production of bread.
- True
Antibiotics are used to cure diseases caused by viruses.
- False
The female Anopheles mosquito is the carrier of the malaria-causing protozoan.
- True
The most common carrier of communicable diseases is the housefly.
- True
Match the Following
Bacteria
(a) Fixing nitrogen
Rhizobium
(b) Setting of curd
Lactobacillus
(c) Baking of bread
Yeast
(d) Causing cholera
Answer the Following Questions
What are microorganisms?
- Microorganisms are tiny living organisms that can only be seen with a microscope. They include bacteria, viruses, fungi, algae, and protozoa.
How do microorganisms play a role in the nitrogen cycle?
- Microorganisms such as bacteria fix nitrogen from the atmosphere into the soil, making it accessible to plants. This process enhances soil fertility.
What is fermentation? Give an example.
- Fermentation is a metabolic process where microorganisms like yeast convert sugars into alcohol or acids. An example is yeast fermenting sugar to produce alcohol in brewing.
Describe the role of microorganisms in the food industry.
- Microorganisms are used in the production of various food products like curd, cheese, bread, and alcoholic beverages. For instance, Lactobacillus bacteria help in setting curd, and yeast is used in baking and brewing.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Which of the following is not a microorganism?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Fungi
(c) Virus
(d) Amoeba
- (d) Amoeba
Which microorganism is used in the making of curd?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Fungi
(c) Algae
(d) Virus
- (a) Bacteria
Additional Questions and Answers
Fill in the Blanks
Protozoa move using hair-like structures called __.
- Cilia
Penicillin was discovered by __.
- Alexander Fleming
Viruses reproduce inside the cells of __.
- Host organisms
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are found in the __ of leguminous plants.
- Root nodules
Fungi are used in the production of __ like bread and cheese.
- Foods
True or False
Viruses can reproduce outside living cells.
- False
Fungi can be both beneficial and harmful.
- True
Protozoa cause diseases like malaria and amoebic dysentery.
- True
Bacteria can only survive in a specific range of environments.
- False
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Which microorganism is known for producing antibiotics?
(a) Virus
(b) Bacteria
(c) Fungi
(d) Algae
- (c) Fungi
Which of the following microorganisms causes tuberculosis?
(a) Virus
(b) Protozoa
(c) Bacteria
(d) Fungi
- (c) Bacteria
Which microorganism is used in baking and brewing?
(a) Algae
(b) Bacteria
(c) Yeast
(d) Virus
- (c) Yeast
Which disease is caused by a virus?
(a) Tuberculosis
(b) Malaria
(c) Influenza
(d) Cholera
- (c) Influenza
Which microorganism helps in nitrogen fixation?
(a) Virus
(b) Fungi
(c) Rhizobium
(d) Algae
- (c) Rhizobium
Answer the Following Questions
What is a pathogen?
- A pathogen is a microorganism that causes disease.
How do vaccines work?
- Vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens, providing immunity.
What is an antibiotic?
- An antibiotic is a substance used to kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria.
Why is the nitrogen cycle important?
- The nitrogen cycle is crucial for converting nitrogen into forms that plants can use for growth, sustaining the ecosystem.
How do microorganisms help in the production of antibiotics?
- Certain microorganisms produce antibiotics naturally to inhibit the growth of other microorganisms.
What role do algae play in the environment?
- Algae produce oxygen through photosynthesis and form the base of aquatic food chains.
What are probiotics?
- Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that help maintain gut health.
How can microorganisms be harmful?
- Microorganisms can cause diseases, spoil food, and contaminate water sources.
What is bioremediation?
- Bioremediation is the use of microorganisms to clean up environmental pollutants.
How do fungi reproduce?
- Fungi reproduce through spores, which can be spread by air, water, or other organisms.