Combustion and Flame: Class 8 NCERT Solutions
This blog post provides solutions to the questions in Chapter 6 “Combustion and Flame” from the NCERT Class 8 Science textbook. Use these detailed answers to understand the concepts better and perform well in your exams.
1. List conditions under which combustion can take place.
Combustion requires:
- Presence of a fuel
- Presence of an oxidizer (usually oxygen)
- An ignition temperature to start the reaction
2. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes pollution of air.
(b) A liquid fuel, used in homes is kerosene.
(c) Fuel must be heated to its ignition temperature before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by water.
3. Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
CNG burns more efficiently and produces fewer pollutants compared to petrol and diesel, leading to reduced emissions of harmful gases such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides.
4. Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
- LPG: Burns more cleanly and efficiently, produces less smoke, and has a higher calorific value.
- Wood: Produces more smoke, causes deforestation, and has a lower calorific value.
5. Give reasons.
(a) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment: Water conducts electricity and can cause electric shocks.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood: LPG burns cleaner, produces more heat, and does not produce smoke.
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily, whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminum pipe does not: Aluminum absorbs heat, preventing the paper from reaching its ignition temperature.
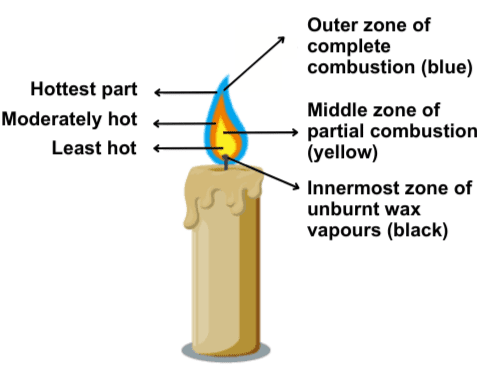
6. Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
[A typical candle flame diagram includes three zones: the innermost zone (dark zone), the middle zone (luminous zone), and the outermost zone (non-luminous zone). You can draw this diagram with proper labels.]
7. Name the unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed.
The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in kilojoules per kilogram (kJ/kg).
8. Explain how CO₂ is able to control fires.
CO₂ displaces oxygen around the fire, reducing the amount of oxygen available for combustion. It is heavier than air and forms a blanket over the flames, smothering the fire.
9. It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain.
Green leaves contain a lot of moisture which makes them difficult to ignite, whereas dry leaves have little to no moisture and can easily reach their ignition temperature.
10. Which zone of a flame does a goldsmith use for melting gold and silver and why?
A goldsmith uses the outermost zone (non-luminous zone) of the flame because it is the hottest part of the flame.
11. Calculate the calorific value of a fuel if 4.5 kg of fuel produced 180,000 kJ of heat when completely burnt.
Calorific value = Total heat produced / Mass of the fuel
Calorific value = 180,000 kJ / 4.5 kg = 40,000 kJ/kg
12. Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
No, rusting cannot be called combustion. Rusting is a slow oxidation process involving iron and oxygen in the presence of moisture, whereas combustion is a rapid oxidation process that releases heat and light.
13. Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time?
Ramesh’s water will get heated in a shorter time because the outermost part of the flame is the hottest zone, providing more heat to the beaker.
Additional Questions
- What is the difference between complete and incomplete combustion?
- Complete combustion occurs in the presence of sufficient oxygen, producing CO₂ and H₂O. Incomplete combustion occurs with limited oxygen, producing CO and soot.
- Why is LPG preferred over kerosene for domestic use?
- LPG burns more cleanly, with a higher calorific value and less smoke compared to kerosene.
- What is spontaneous combustion?
- Spontaneous combustion is the self-ignition of a material without an external flame due to internal heat buildup.
- How does a fire extinguisher work?
- A fire extinguisher works by cooling the burning material, cutting off the supply of oxygen, or stopping the chemical reaction of the fire.
- Explain the concept of the ignition temperature.
- Ignition temperature is the minimum temperature at which a substance catches fire and undergoes combustion.
- Why is water not effective in extinguishing oil fires?
- Water is heavier than oil and sinks below it, allowing the oil to continue burning on the surface.
- What is the role of an oxidizer in combustion?
- An oxidizer provides the necessary oxygen for the fuel to combust.
- How do fire blankets work?
- Fire blankets smother the fire by cutting off the oxygen supply.
- Why do firefighters use foam to extinguish fires?
- Foam covers the burning material and prevents oxygen from reaching the fire, thereby extinguishing it.
- What is a fire triangle?
- A fire triangle illustrates the three components needed for fire: fuel, oxygen, and heat.
- What is meant by flash point?
- Flash point is the lowest temperature at which a liquid can form an ignitable mixture in air.
- Describe the characteristics of the three zones of a candle flame.
- Innermost zone: least hot, dark.
- Middle zone: moderately hot, luminous.
- Outermost zone: hottest, non-luminous.
- How can you distinguish between a fire caused by electrical equipment and other fires?
- Electrical fires involve live electrical equipment and may produce sparks.
- Why should inflammable materials be stored carefully?
- Inflammable materials have low ignition temperatures and can catch fire easily.
- What are fire-resistant materials?
- Fire-resistant materials are designed to withstand high temperatures and resist burning.
- Explain the importance of fire safety measures in buildings.
- Fire safety measures prevent the spread of fire, ensure safe evacuation, and reduce property damage.
- How does the presence of moisture affect combustion?
- Moisture lowers the temperature and slows down or prevents combustion.
- What is the significance of calorific value in fuels?
- Calorific value indicates the amount of energy produced by burning a specific amount of fuel.
- What happens during the combustion of hydrocarbons?
- Combustion of hydrocarbons produces CO₂, H₂O, and energy.
- Why is hydrogen considered a clean fuel?
- Hydrogen produces only water vapor when it burns, emitting no pollutants.
- What are the by-products of incomplete combustion?
- Incomplete combustion produces CO, soot, and other harmful substances.
- How can you prevent accidental fires at home?
- By keeping inflammable materials away from heat sources, ensuring proper ventilation, and using fire alarms.
- What is a backdraft in fire dynamics?
- A backdraft is an explosion caused by the sudden introduction of oxygen into an oxygen-deprived environment containing hot gases.
- How does air supply affect the color of a flame?
- Adequate air supply results in a blue flame, while limited air supply produces a yellow flame.
- Why should you never use water to extinguish a grease fire?
- Water can cause the grease to splatter and spread the fire.
- What role do fire drills play in fire safety?
- Fire drills prepare individuals to respond quickly and effectively in case of a fire emergency.
- What is the purpose of a fire sprinkler system?
- Fire sprinklers automatically release water to suppress or extinguish fires.
- How does a smoke detector work?
- Smoke detectors sense smoke particles in the air and trigger an alarm.
- What precautions should be taken while using fireworks?
- Use fireworks in open spaces, keep a safe distance, and have fire extinguishing means ready.
- How can forest fires be prevented?
- By monitoring weather conditions, clearing dry vegetation, and following fire safety regulations.
For further understanding and detailed explanations, refer to your NCERT Class 8 Science textbook and other reliable educational resources.
Combustion and Flame: Class 8th Science Notes
Textual questions of Combustion and Flame chapter of the class 8th
What is Combustion?
Combustion is a chemical process where a substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light. This process typically results in the formation of oxides and the release of energy.
Example:
- Burning of wood: C + O2 – – – – – – > CO2 + Heat
Types of Combustion
1. Rapid Combustion
Occurs quickly and produces heat and light.
Example:
- Lighting a matchstick.
2. Spontaneous Combustion
Occurs without an external ignition source due to the self-heating of materials.
Example:
- Phosphorus burning in air.
3. Explosive Combustion
Occurs with a rapid release of gases and energy, often causing an explosion.
Example:
- Firecrackers bursting.
How Do We Control Fire?
Fire control involves removing one or more elements of the fire triangle: heat, fuel, and oxygen.
Methods:
- Cooling the Fire: Use water to lower the temperature.
- Removing the Fuel: Clear combustible materials from the vicinity of the fire.
- Cutting Off Oxygen: Use fire extinguishers or fire blankets to smother the fire.
Flame
A flame is the visible part of a fire, consisting of glowing gases emitted during combustion.
Structure of a Flame
- Outer Zone: Blue, hottest part, complete combustion.
- Middle Zone: Yellow, partial combustion.
- Inner Zone: Dark, least hot, contains unburnt fuel vapors.
Illustration:
What is a Fuel?
A fuel is any substance that can undergo combustion to produce heat and energy.
Examples:
- Coal
- Wood
- Petrol
- Natural Gas
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a measure of how much energy a fuel releases per unit mass. It is expressed as calorific value.
Example:
- Calorific value of petrol: 47,000 kJ/kg
Conditions for Combustion
Combustion requires:
- Presence of a fuel.
- Availability of oxygen.
- Reaching the ignition temperature.
Fill in the Blanks( Combustion and Flame)
- (a) Burning of wood and coal causes pollution of air.
(b) A liquid fuel, used in homes is kerosene.
(c) Fuel must be heated to its ignition temperature before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by water.
Reducing Pollution with CNG
The use of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) in automobiles has reduced pollution as CNG burns cleaner than petrol or diesel, emitting fewer pollutants and greenhouse gases.
Comparing LPG and Wood as Fuels
LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas)
- Higher calorific value.
- Produces less smoke and pollutants.
- Easy to store and transport.
- Burns efficiently with a blue flame.
Wood
- Lower calorific value.
- Produces more smoke and pollutants.
- Requires more storage space.
- Burns with a yellow flame, can produce soot.
Reasons and Explanations (Combustion and Flame)
- Water and Electrical Fires: Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment because it conducts electricity, leading to electric shocks or short circuits.
- LPG vs. Wood: LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood because it has a higher calorific value, burns more efficiently, and produces less smoke.
- Paper and Aluminium: Paper catches fire easily because it has a low ignition temperature. A piece of paper wrapped around an aluminum pipe does not catch fire easily because the metal absorbs the heat, preventing the paper from reaching its ignition temperature.
Diagram of a Candle Flame
Insert a labelled diagram of a candle flame with the following zones:
- Outer Zone: Blue, hottest part, complete combustion.
- Middle Zone: Yellow, partial combustion.
- Inner Zone: Dark, least hot, unburnt vapors.
Calorific Value Unit
The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in kilojoules per kilogram (kJ/kg).
CO2 for Fire Control
Carbon dioxide (CO2) controls fires by displacing oxygen around the fire, suffocating it, and stopping the combustion process.
Burning of Leaves
Green leaves contain moisture, making it difficult to reach ignition temperature. Dry leaves lack moisture, making them easier to ignite and burn.
Goldsmith’s Flame Zone
A goldsmith uses the outermost zone of a flame for melting gold and silver because it is the hottest part, providing the necessary high temperature for melting metals.
Calculating Calorific Value
In an experiment, 4.5 kg of fuel produced 180,000 kJ of heat. The calorific value is calculated as:
Total heat produced / Mass of Fuel
180,000/4.5 = 40,000 kJ/kg.
Rusting vs. Combustion
Rusting is a slow process and does not produce heat and light, unlike combustion, which is a fast process that releases heat and light. Therefore, rusting cannot be called combustion.
Heating Experiment
Ramesh’s water will heat faster because the outermost part of the flame is the hottest and provides more heat energy compared to the yellow part of the flame where Abida placed her beaker.