 >
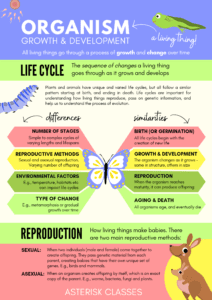
>Reproduction is a fundamental process by which organisms produce offspring, ensuring the continuation of their species. There are two main types of reproduction: asexual and sexual. Let’s delve into the detailed structure and function of each type, along with their differences and similarities.
Introduction to Reproduction
Reproduction allows organisms to pass on their genetic material to the next generation. This process can occur in two primary ways: asexually or sexually, each with unique mechanisms and characteristics.
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction involves a single parent and results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.
Types of Asexual Reproduction:
- Binary Fission: Common in prokaryotes, where a single organism divides into two equal parts. Example: Bacteria.
- Budding: A new organism grows out of the body of the parent organism. Example: Yeast.
- Fragmentation: An organism breaks into fragments, each capable of growing into a new individual. Example: Starfish.
- Vegetative Propagation: New plants grow from parts of the parent plant, such as roots, stems, or leaves. Example: Potato tubers.
- Spore Formation: Organisms produce spores that can develop into new individuals. Example: Fungi.
Function:
- Produces genetically identical offspring.
- Allows rapid population growth in favorable conditions.
Amazing Fact:
- Some bacteria can reproduce every 20 minutes under optimal conditions!
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes, resulting in offspring with genetic variation.
Structure and Process:
- Gametes: Specialized sex cells (sperm in males and eggs in females) are produced through meiosis.
- Fertilization: The fusion of sperm and egg results in a zygote, which develops into a new organism.
- Development: The zygote undergoes multiple divisions and differentiation to form a complete organism.
Function:
- Produces genetically diverse offspring.
- Enhances adaptability and survival in changing environments.
Amazing Fact:
- Human beings can produce about 8.4 million different combinations of genes from their parents!
Differences Between Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
Genetic Variation:
- Asexual: Offspring are genetically identical to the parent.
- Sexual: Offspring have genetic variation due to the combination of genes from both parents.
Number of Parents:
- Asexual: Involves a single parent.
- Sexual: Involves two parents.
Speed and Efficiency:
- Asexual: Faster and more efficient, leading to rapid population growth.
- Sexual: Slower due to the need for gamete production and fertilization.
Adaptability:
- Asexual: Less adaptable to environmental changes due to lack of genetic variation.
- Sexual: More adaptable due to genetic diversity.
Similarities Between Asexual and Sexual Reproduction
Purpose:
- Both types aim to produce offspring and ensure the survival of the species.
Basic Process:
- Involve the creation of new individuals from existing organisms.
Cell Division:
- Both involve cell division processes (mitosis in asexual and meiosis in sexual reproduction).
Life Cycle:
- Both contribute to the life cycle of organisms, allowing them to grow, develop, and reproduce.
Fascinating Facts About Reproduction
- Cloning: Some plants and animals can naturally clone themselves through asexual reproduction.
- Genetic Diversity: Sexual reproduction introduces genetic diversity, which is crucial for the evolution of species.
- Parthenogenesis: Some animals, like certain reptiles and insects, can reproduce through parthenogenesis, where females produce offspring without fertilization by a male.
Understanding reproduction highlights the diversity of life and the strategies organisms use to perpetuate their species. Whether through the simplicity of asexual reproduction or the complexity of sexual reproduction, life continues to adapt and thrive in an ever-changing world.

