The power of accommodation is the ability of the eye to focus on nearby and distant objects by adjusting the focal length of the lens.
Power of Accommodation
What is Power of Accommodation?
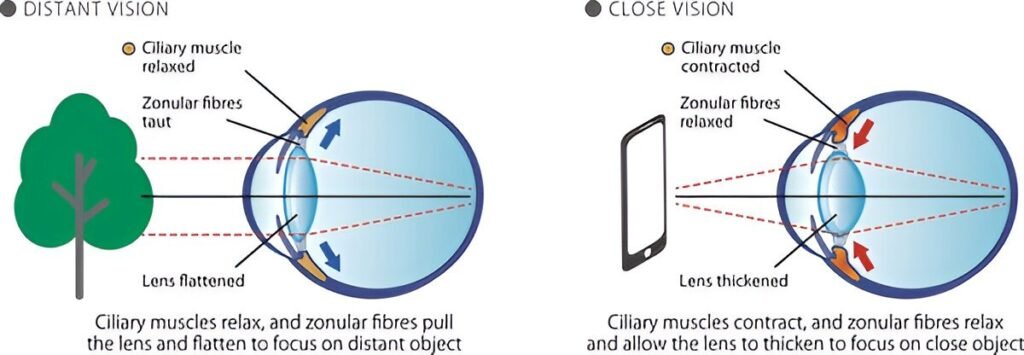
The power of accommodation is the ability of the eye to focus on nearby and distant objects by adjusting the focal length of the lens. This is achieved by changing the shape of the eye’s lens with the help of the ciliary muscles.
- When the ciliary muscles contract, the lens becomes thicker and more convex, increasing its refractive power to focus on nearby objects.
- When the ciliary muscles relax, the lens becomes thinner and less convex, decreasing its refractive power to focus on distant objects.
The power of accommodation is measured in diopters (D). A normal human eye has a power of accommodation of about 4 diopters.
Examples of Power of Accommodation
Example 1: Reading a Book
When you read a book, your eyes focus on the text, which is close to you. The ciliary muscles contract, making the lens thicker to increase its refractive power and focus the light rays on the retina.
Example 2: Looking at a Distant Mountain
When you look at a distant mountain, your eyes focus on the faraway object. The ciliary muscles relax, making the lens thinner to decrease its refractive power and focus the light rays on the retina.
Problems and Solutions (NCERT Based)
Problem 1: A person cannot see nearby objects clearly. What is this defect called, and how can it be corrected?
Solution: This defect is called hypermetropia (far-sightedness). It occurs when the eye cannot focus on nearby objects due to the lens being unable to become sufficiently convex. It can be corrected using a convex lens of appropriate power.
Problem 2: A person cannot see distant objects clearly. What is this defect called, and how can it be corrected?
Solution: This defect is called myopia (near-sightedness). It occurs when the eye cannot focus on distant objects due to the lens being unable to become sufficiently thin. It can be corrected using a concave lens of appropriate power.
Problem 3: A person has a power of accommodation of 2 diopters. What does this mean?
Solution: A power of accommodation of 2 diopters means that the person’s eye can adjust its focal length to focus on objects within a range of 50 cm to infinity. This is calculated using the formula:
Range of Vision = 1 / Power of Accommodation
For example, 1 / 2 D = 0.5 meters (50 cm).
Key Points to Remember
- The power of accommodation decreases with age, leading to a condition called presbyopia.
- The minimum distance at which the eye can focus clearly is called the near point (about 25 cm for a normal eye).
- The farthest point at which the eye can focus clearly is called the far point (infinity for a normal eye).
- The power of accommodation is essential for clear vision at varying distances.