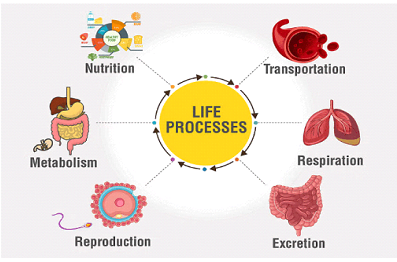
Glass Prism: Refraction and Dispersion
What is a Glass Prism?
A glass prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. It is typically triangular in shape and is used to study the phenomena of refraction and dispersion of light.
Refraction of Light
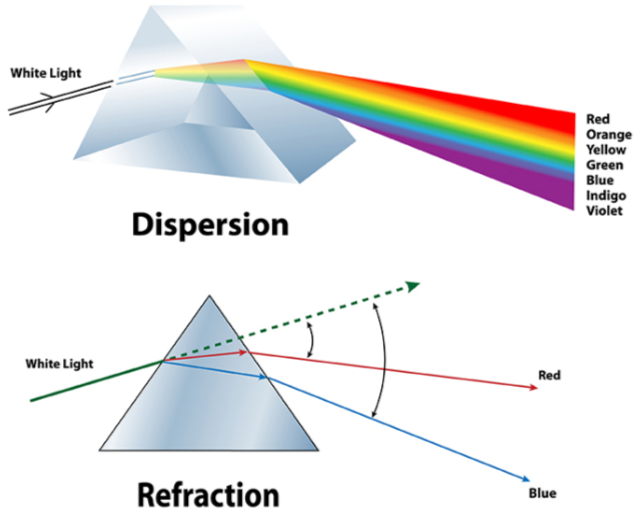
Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another with a different optical density. This occurs because light travels at different speeds in different media.
Refraction in a Prism
When light enters a prism, it bends towards the base of the prism due to refraction. When it exits the prism, it bends again, but away from the base.
 >
>The amount of bending depends on the angle of incidence and the refractive index of the prism material.
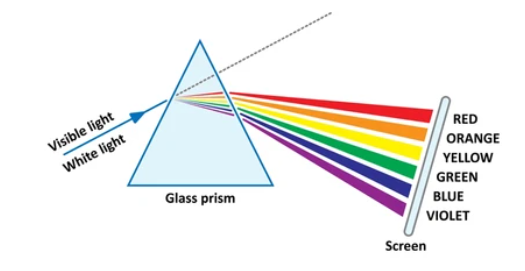
Dispersion of Light
Dispersion is the splitting of white light into its constituent colors (VIBGYOR: Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red) when it passes through a prism. This happens because different colors of light travel at different speeds in the prism and are refracted by different angles.
Dispersion in a Prism
When white light enters a prism, it is dispersed into a spectrum of colors. Violet light bends the most, while red light bends the least.
 >
>This phenomenon is responsible for the formation of rainbows in nature.
Working of a Glass Prism
A glass prism works on the principles of refraction and dispersion. Here’s how it works:
- White light enters the prism through one of its faces.
- The light is refracted (bent) as it enters the prism.
- Inside the prism, the light is dispersed into its constituent colors.
- The dispersed light is refracted again as it exits the prism.
- The result is a spectrum of colors emerging from the prism.
Working of a Glass Prism
 >
>Examples of Refraction and Dispersion
Example 1: Rainbow Formation
A rainbow is formed when sunlight is refracted, dispersed, and reflected by water droplets in the atmosphere. Each droplet acts like a tiny prism.
 >
>Example 2: Prism in a Spectrometer
A prism is used in a spectrometer to analyze the spectrum of light emitted by different sources, such as stars or chemical elements.
Key Points to Remember
- Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another.
- Dispersion is the splitting of white light into its constituent colors.
- A glass prism uses refraction and dispersion to create a spectrum of colors.
- Violet light bends the most, and red light bends the least during dispersion.
- Rainbows are a natural example of dispersion caused by water droplets.