Sexual reproduction in flowering plants notes
Complete Class 12 Notes with Diagrams
Introduction
Flowering plants (angiosperms) reproduce sexually through specialized reproductive structures called flowers. This process involves the formation of male and female gametes, their transfer via pollination, and subsequent fertilization leading to seed formation.
Key Features:
- Flowers are modified shoots with specialized reproductive organs
- Process involves both haploid (gametophyte) and diploid (sporophyte) generations
- Unique double fertilization mechanism in angiosperms
- Results in formation of seeds enclosed in fruits
Flower Structure
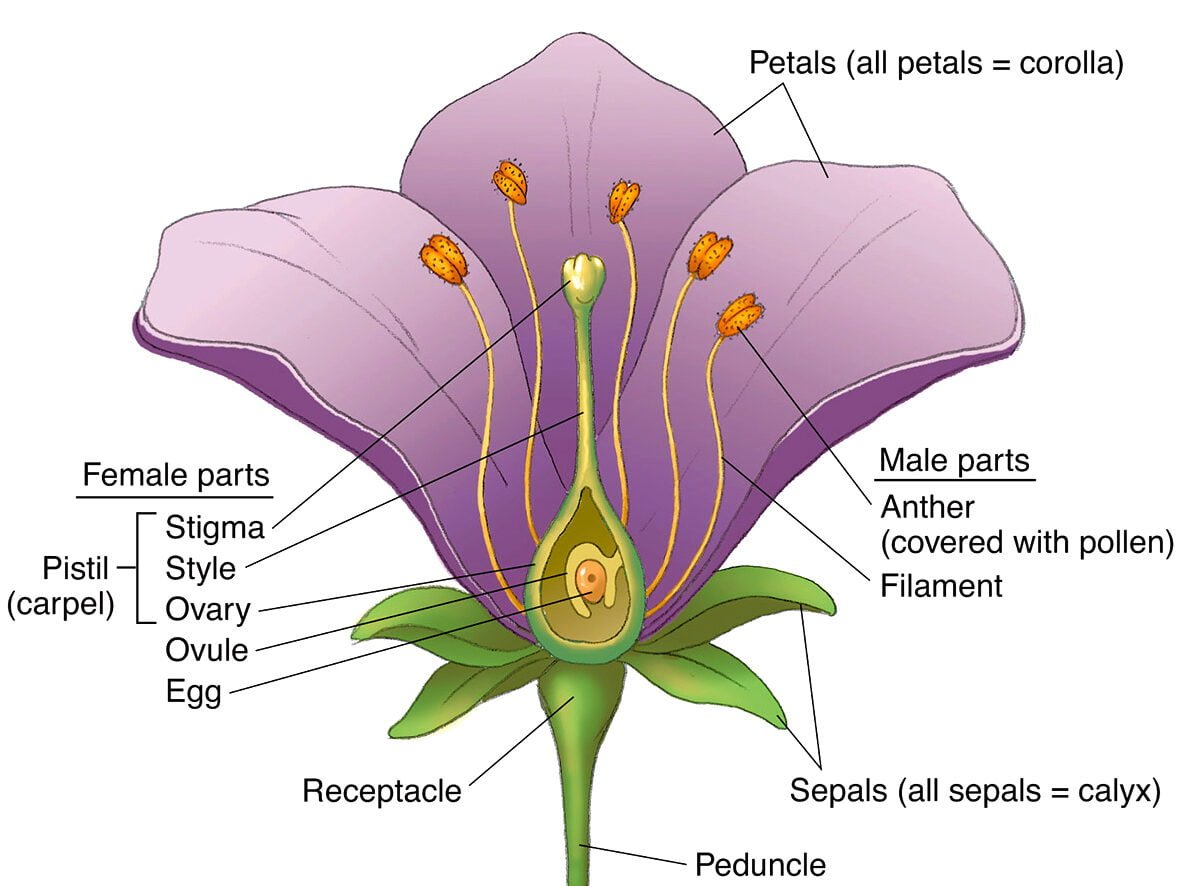
Typical flower structure showing reproductive parts
Male Reproductive Parts (Androecium):
- Stamen: Anther + Filament
- Anther: Bilobed structure with microsporangia (pollen sacs)
- Pollen grain: Male gametophyte (2-celled or 3-celled stage)
- Development: Microsporogenesis → Microspores → Pollen grains
Female Reproductive Parts (Gynoecium):
- Pistil: Stigma + Style + Ovary
- Ovule: Contains megasporangium (nucellus) with embryo sac
- Embryo sac: 7-celled 8-nucleate structure (female gametophyte)
- Development: Megasporogenesis → Megaspore → Embryo sac
Complete Chapter Notes
Access the detailed notes I’ve prepared covering all NCERT concepts, reactions, and important questions:
Pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma of a flower
Types of Pollination:
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Autogamy | Self-pollination within same flower | Pea, Commelina |
| Geitonogamy | Between different flowers of same plant | Maize |
| Xenogamy | Between flowers of different plants | Most flowering plants |
Pollination Agents:
1. Anemophily (Wind)
Small, light, non-sticky pollen
Large feathery stigmas
Example: Grasses
2. Entomophily (Insects)
Bright flowers with nectar
Sticky pollen, fragrant
Example: Sunflower
3. Hydrophily (Water)
Pollen released underwater
Long ribbon-like stigmas
Example: Vallisneria
Fertilization Process
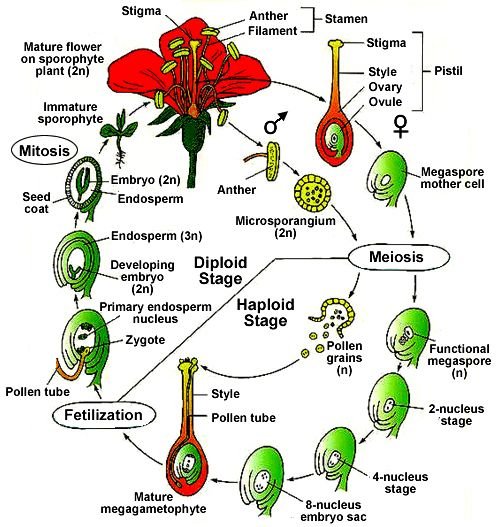
Double fertilization in angiosperms
Pollen-Pistil Interaction:
- Pollen lands on stigma and hydrates
- Pollen tube grows through style towards ovary
- Generative cell divides to form two male gametes
- Pollen tube enters ovule through micropyle
Double Fertilization:
1. Syngamy
One male gamete (n) fuses with egg (n) → forms zygote (2n) which develops into embryo
2. Triple Fusion
Second male gamete (n) fuses with two polar nuclei (n+n) → forms primary endosperm nucleus (3n) which develops into endosperm (nutritive tissue)
Post-Fertilization Changes
Ovule → Seed:
- Integuments: Develop into seed coat
- Zygote: Develops into embryo (with radicle, plumule, cotyledons)
- Endosperm: Provides nutrition (may be consumed by embryo in dicots)
- Micropyle: Small pore for water absorption during germination
Ovary → Fruit:
- Pericarp: Fruit wall develops from ovary wall
- May be fleshy (mango) or dry (pea)
- True fruit develops only from ovary (e.g., mango)
- False fruit develops from other floral parts (e.g., apple)
Special Cases:
- Parthenocarpy: Fruit formation without fertilization (seedless fruits)
- Apomixis: Seed formation without fertilization (e.g., some grasses)
- Polyembryony: Multiple embryos in one seed (e.g., citrus, mango)
NCERT Important Questions
Q. Explain the process of microsporogenesis in angiosperms.
Microsporogenesis is the formation of microspores from microspore mother cells (MMC) through meiosis:
- MMC (2n) in microsporangium undergoes meiosis
- Forms microspore tetrad (4 haploid microspores)
- Microspores separate and develop into pollen grains
- Pollen grain undergoes mitosis to form vegetative and generative cells
Q. What is triple fusion? Where does it occur?
Triple fusion is the fusion of:
- One male gamete (n) with two polar nuclei (n+n) in the central cell
- Forms primary endosperm nucleus (3n)
- Occurs in the embryo sac of ovule
- Results in formation of triploid endosperm
Quick Revision Table
| Structure | Develops Into | Ploidy |
|---|---|---|
| Zygote | Embryo | 2n |
| Primary endosperm nucleus | Endosperm | 3n |
| Integuments | Seed coat | 2n |
| Ovary wall | Pericarp (fruit wall) | 2n |
| Nucellus | Perisperm (in some seeds) | 2n |
Download Complete Notes
Get printable PDF with diagrams, NCERT solutions, and important questions