The Cell: The Building Block of Life
Introduction
The cell is the fundamental unit of life, a marvel of biological architecture that orchestrates the complex symphony of life processes. It is the smallest unit capable of performing life functions, making it crucial for the existence of all living organisms. This blog post delves into the intricate world of cells, exploring their importance and the roles they play in sustaining life.
The Structural Significance of Cells
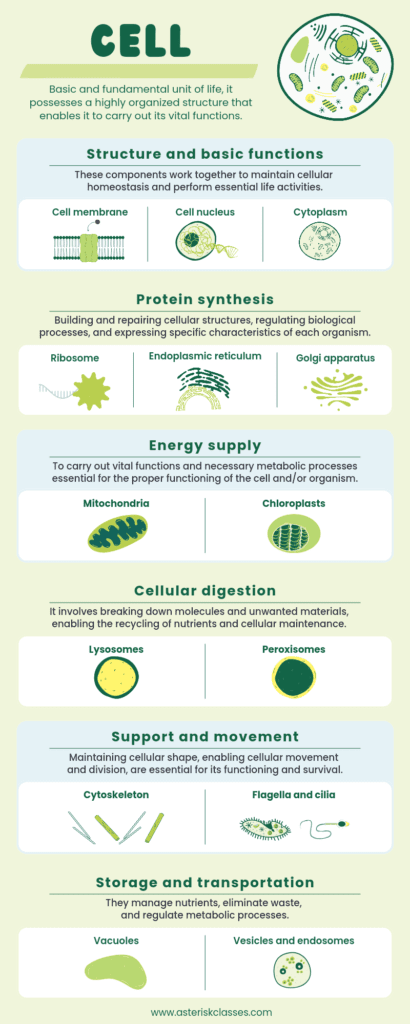
Cells are the basic structural units of all living organisms. From the tiniest bacteria to the largest whales, every organism is composed of cells. The human body, for instance, contains trillions of cells, each specialized to perform specific functions. These cells work in unison to form tissues, which in turn create organs and organ systems, culminating in the complex beings that we are.
Functional Mastery of Cells
Functionally, cells are the workhorses of life. They carry out essential processes such as metabolism, where they convert nutrients into energy, and synthesis, where they create the molecules necessary for life. Cells also play a pivotal role in reproduction, passing genetic information to the next generation through cell division.
Examples of Cellular Functions
- Energy Production: Mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, generate ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
- Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis, translating genetic information into functional proteins.
- Waste Elimination: Lysosomes are cellular organelles that digest waste materials and cellular debris.
Diseases and Cellular Dysfunction
When cellular components malfunction, it can lead to diseases. For example:
- Pompe Disease: A genetic disorder resulting from the buildup of glycogen in cells, particularly muscle cells.
- Leigh Disease: A severe neurological condition caused by lesions in the brain, affecting cellular energy production.
- Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy: A condition characterized by muscle weakness linked to defects in the cellular structure.
The Unseen Heroes: Cellular Components
Cells are composed of various components, each with a unique function:
- Cell Membrane: Acts as a barrier, controlling the entry and exit of substances.
- Nucleus: Houses genetic material and controls cellular activities.
- Cytoplasm: The jelly-like substance where organelles reside, facilitating their functions.
Conclusion
Cells are the essence of life, performing a myriad of tasks that sustain the living world. Understanding cells and their functions not only sheds light on the complexity of life but also paves the way for advancements in medicine and biotechnology. As we continue to explore the cellular universe, we uncover more about our own existence and the intricate web of life that binds us all.