Life processes are essential activities that living organisms carry out to maintain their existence, grow, reproduce, and respond to their environment. These processes are fundamental to the functioning of living organisms and are necessary for their survival
The major life processes include:
⦁ Nutrition: Nutrition involves the intake, digestion, absorption, and utilization of nutrients by organisms to obtain energy and raw materials for growth, repair, and maintenance. It can be autotrophic (organisms produce their own food, like plants through photosynthesis) or heterotrophic (organisms obtain food from other sources).
⦁ Respiration: Respiration is the process by which organisms obtain energy from nutrients (such as glucose) through the breakdown of complex molecules, typically with the consumption of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide as a byproduct. Respiration occurs in both aerobic (with oxygen) and anaerobic (without oxygen) conditions.
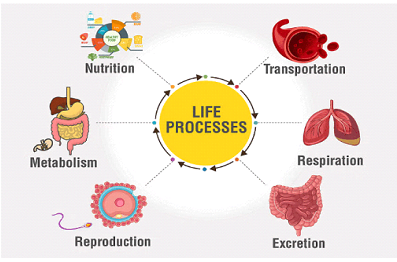 >
>Transportation: Transportation involves the movement of substances such as nutrients, gases, and wastes within the organism’s body. In multicellular organisms, transportation occurs through specialized systems like the circulatory system in animals and the vascular system in plants.
⦁ Excretion: Excretion is the removal of metabolic wastes and excess substances from the organism’s body. This process helps maintain internal homeostasis by eliminating harmful substances and regulating the composition of body fluids. Excretory organs, such as the kidneys in animals and specialized cells in plants, facilitate excretion.
⦁ Reproduction: Reproduction is the process by which organisms produce offspring, ensuring the continuation of their species. It can occur through sexual or asexual means, involving the formation and fusion of gametes (sex cells) or the production of genetically identical clones, respectively.



