Most IImportant Raw material for the Photosynthesis are as :
The Marvel of Photosynthesis: Nature’s Ingenious Solar-Powered Factories
Photosynthesis is a remarkable biochemical process that is fundamental to life on Earth. It allows plants, algae, and some bacteria to convert light energy into chemical energy, fueling their existence and forming the base of the food web. Here we explore the steps of photosynthesis and share some fascinating facts about this vital process.
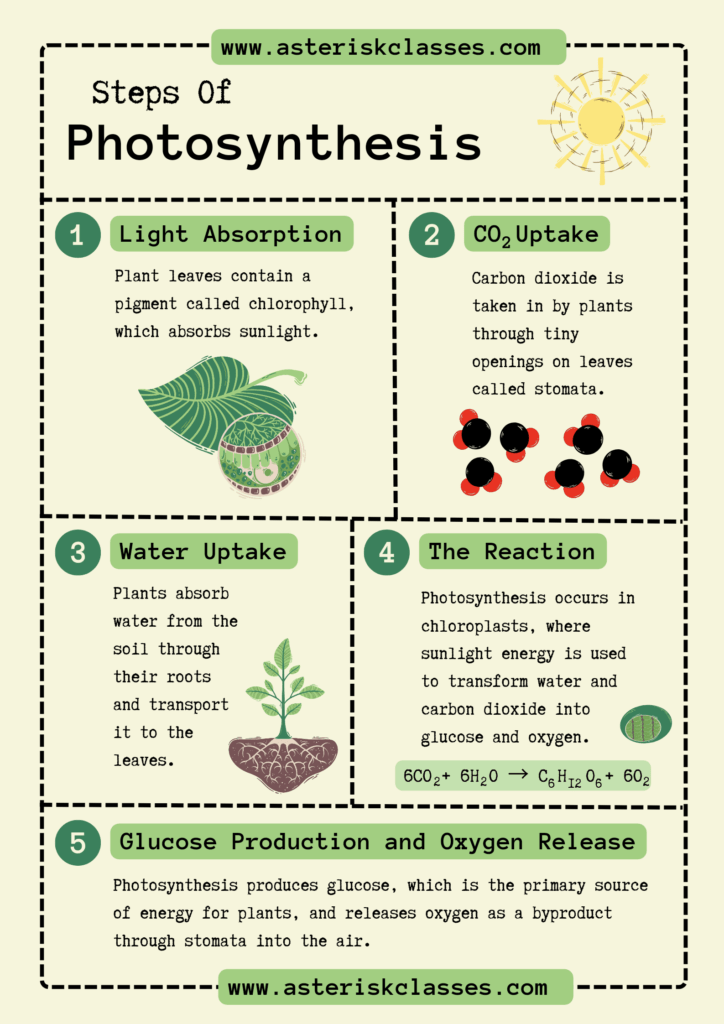
The Steps of Photosynthesis
1. Light Absorption
The journey of photosynthesis begins with the absorption of light. Plants have specialized structures called chloroplasts that contain pigments like chlorophyll. These pigments capture the energy from sunlight, which is crucial for the subsequent steps.
2. Water Splitting (Light-Dependent Reactions)
In the presence of light, water molecules within the chloroplasts are split apart, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. This stage also generates ATP and NADPH, which are energy carriers used in the next phase of photosynthesis.
3. Carbon Fixation (Light-Independent Reactions)
The ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions are used in the Calvin cycle, a series of reactions that occur in the stroma of chloroplasts. Here, carbon dioxide is fixed into glucose, a simple sugar that plants use for energy and growth.
Interesting Facts About Photosynthesis
- Not Just for Energy: While glucose is primarily used for energy, it also serves as a building block for more complex molecules like starch and cellulose, which are essential for the plant’s structure and energy storage.
- Chlorophyll’s Central Role: Chlorophyll is the most well-known pigment for photosynthesis, giving plants their green color. It’s adept at capturing solar energy, but it’s not the only pigment involved. Other pigments like carotenoids also play a role in capturing light energy.
- Oxygen’s Vital Release: Photosynthesis is responsible for producing the oxygen we breathe. It’s estimated that about 50-85% of the world’s oxygen is produced via photosynthesis from oceanic plankton and terrestrial plants.
- Adaptations for Efficiency: Leaves are the primary sites of photosynthesis in plants, and they have evolved to maximize efficiency. Their large surface area, thin structure, and abundance of chlorophyll ensure that light absorption and gas exchange occur effectively.
- Ancient Process: Photosynthesis has been shaping our planet for billions of years. The oxygen-rich atmosphere we enjoy today is largely due to the photosynthetic activities of ancient microorganisms.
- Varied Methods: Not all photosynthesis is the same. Some plants, like those in arid environments, have adapted a special form of photosynthesis known as CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) to minimize water loss.
Photosynthesis is not just a scientific phenomenon; it’s a lifeline that sustains ecosystems and balances our atmosphere. Its intricate steps and the fascinating facts surrounding it remind us of the complex beauty of the natural world.