Nature and Structure
Electric charge, like mass and length, is a fundamental property of matter. Atoms, the building blocks of matter, are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. Electrons carry a negative charge, protons carry a positive charge, and neutrons are neutral.
Atomic Structure
- Nucleus: Contains positively charged protons and neutral neutrons.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus.
In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons. When an electron is removed, the atom becomes a positively charged ion. Conversely, adding an extra electron results in a negatively charged ion.
Example: Charging by Friction
When a plastic comb is rubbed against dry hair, electrons transfer from the hair to the comb:
- Comb: Gains electrons, becomes negatively charged.
- Hair: Loses electrons, becomes positively charged.
Measuring Electric Charge
- Unit: Coulomb (C)
- Electron Charge: -1.6 × 10-19 C
- Formula: q = ne (where n is an integer)
Additive Nature
Electric charge is additive. The total charge in a system is the algebraic sum of individual charges. For example:
- Charges: +5C and −2C
- Total Charge: (+5C)+(−2C)=+3C
Electric Field
An electric field is a region around a charge where another charge experiences a force. Represented by field lines with arrowheads indicating the direction:
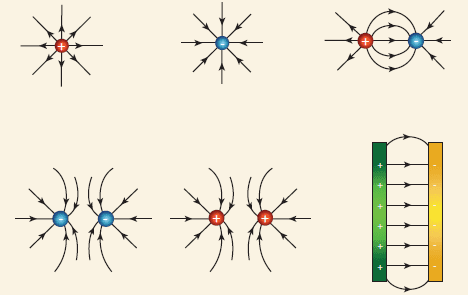 >
>- Positive Charge: Field lines radiate outward.
- Negative Charge: Field lines radiate inward.
Electric Lines of Force
- Direction: Path a positive test charge would move.
- Nature: Imaginary lines indicating field strength and direction. Closer lines indicate stronger fields.
Electric Force
Two types of electric force exist between charges:
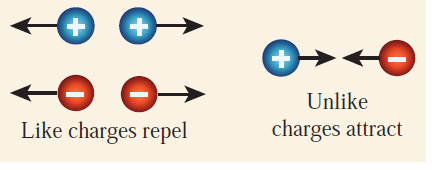 >
>- Attractive Force: Between unlike charges (positive and negative).
- Repulsive Force: Between like charges (positive-positive or negative-negative).