 >
>The Vital Role of Plants Reproduction: Types and Significance
Introduction
Plants Reproduction is a fundamental biological process that ensures the survival and diversity of plant species. Through reproduction, plants produce offspring, pass on genetic information, and contribute to the ecological balance. This blog post explores the various types of plant reproduction and delves into why this process is crucial for plants and the environment.
Types of Plants Reproduction
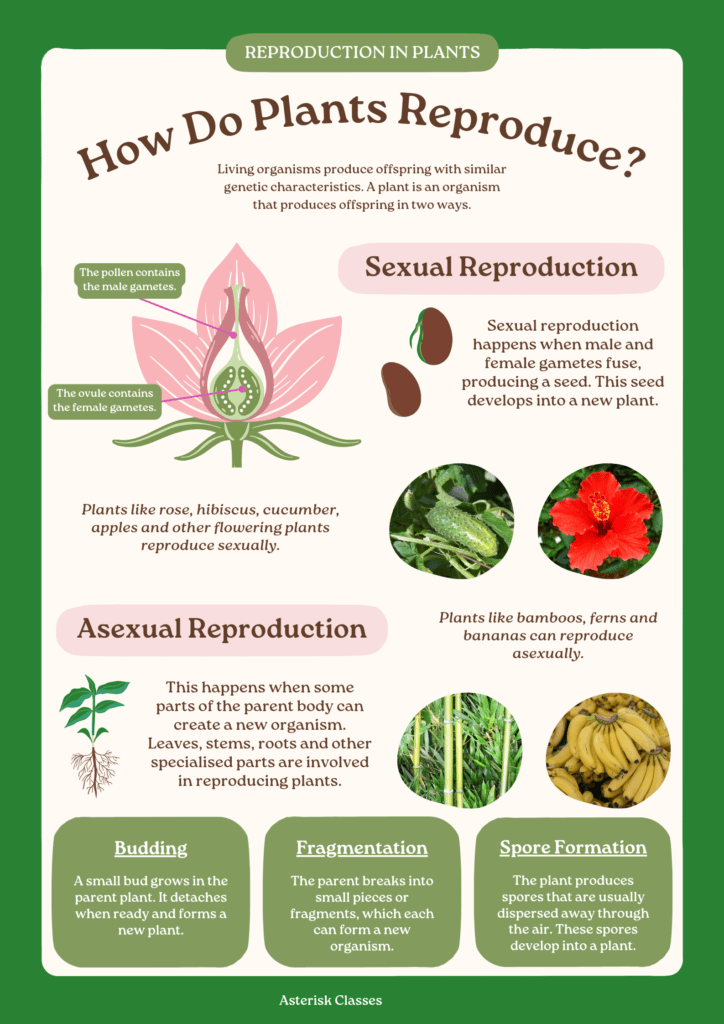
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction in plants is a process where offspring are produced from a single parent, without the involvement of gametes or seeds. This type of reproduction results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent, known as clones.
Methods of Asexual Reproduction
- Budding: An outgrowth from a cell that eventually detaches to form a new plant.
- Fragmentation: A piece or fragment of the plant breaks off and develops into a new plant.
- Fission: A single cell divides into two or more parts, each growing into a complete plant.
- Vegetative Reproduction: New plants grow from non-reproductive structures like stems, roots, or leaves.
- Apomixis: Seeds are produced without fertilization, bypassing the sexual reproduction process.
- Spore Formation: Haploid reproductive units called spores develop into new plants without fertilization.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction involves the combination of genetic material from two parents, resulting in offspring with genetic variation. This type of reproduction is essential for the evolution and adaptation of plant species.
Flowering Plants (Angiosperms)
In angiosperms, the flower is the reproductive organ. They reproduce through a process called double fertilization, where the male and female gametes unite to form seeds within the fruit.
Importance of Plants Reproduction
Genetic Diversity
Sexual reproduction introduces genetic variation, which is vital for the adaptation and survival of plant species. It allows plants to cope with changing environmental conditions and resist diseases and pests.
Ecosystem Balance
Plants are primary producers in ecosystems, and their reproduction ensures the continuity of food chains. They provide habitat and food for numerous organisms, playing a critical role in maintaining biodiversity.
Agricultural and Horticultural Advancements
Understanding plant reproduction can lead to improvements in crop yields and the development of new plant varieties. It also aids in the conservation of plant species and the restoration of degraded habitats.
Environmental Sustainability
Plants contribute to the stabilization of ecosystems by reproducing and spreading across landscapes. They help in soil formation, nutrient cycling, and carbon sequestration, combating climate change.
Conclusion
The study of plant reproduction is not only fascinating but also essential for the sustainability of our natural world. By comprehending the mechanisms and importance of plant reproduction, we can better appreciate the intricate connections within ecosystems and the vital role plants play in our lives.
Understanding plant reproduction is a step towards a greener, more sustainable future. Whether it’s the asexual propagation of a houseplant or the complex sexual reproduction of a forest tree, each process contributes to the rich tapestry of life on Earth.